Sun and vitamin D
-
A bit of sun can help our bodies make vitamin D, which is important to keep bones, teeth and muscles healthy.
-
You don’t need to sunbathe to get enough vitamin D. Most people in the UK can make enough by spending short periods of time in the sun.
-
If you are worried about vitamin D deficiency, speak to your doctor.
Our bodies need vitamin D to keep bones, teeth and muscles healthy. Low levels of vitamin D (vitamin D deficiency) can cause health problems. These include bone problems in adults, and rickets (bone deformities) in children.
Do I need to sunbathe to get enough vitamin D?
No, you don’t need to sunbathe to get enough vitamin D.
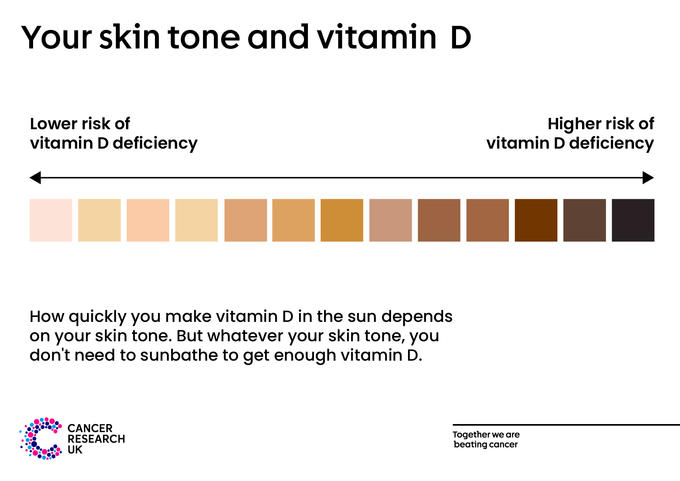
A bit of sun helps our bodies to make vitamin D. The amount of sunlight we need to make vitamin D in the UK is different for each person. It depends on your skin tone and the time of day or year.
Between mid-March and mid-October, short breaks in the sun should be enough for most people to make all the vitamin D they need. But remember, too much sun can cause sunburn and increase the risk of skin cancer. Learn about how to enjoy the sun safely.
We can also get vitamin D in our diet, from foods such as:
- egg yolks
- fresh or tinned oily fish (for example, mackerel or sardines)
- fish liver oils
- some margarines
- fortified cereals, which have vitamins and minerals added
Should I take a vitamin D supplement?
In the UK, the NHS recommends people at risk of vitamin D deficiency take a 10 microgram (400 I.U.) supplement throughout the year.
People who are at higher risk of vitamin D deficiency include:
- People with naturally darker skin tones, such as brown or black skin
- People who spend very little time in the sun. For example, those who are housebound or in care homes
- People who usually wear clothes that cover up most of their skin when outdoors
- People over the age of 65
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women
- Babies and children aged under 4
The NHS also recommends that everyone takes a 10 microgram vitamin D supplement between October and March, when the sun’s rays are weaker.
Read more about NHS guidance on vitamin D supplements.
Does vitamin D deficiency cause cancer?
There isn’t enough convincing evidence to link low levels of vitamin D (vitamin D deficiency) to cancer. And there’s not evidence to support taking vitamin D supplements to reduce cancer risk.
But vitamin D deficiency can cause other health conditions, including rickets in children and bone problems in adults. If you are worried vitamin D deficiency, speak to your doctor.
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Sunlight exposure: risks and benefits. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng34/chapter/supporting-information-for. [Accessed April 2024]
International Agency for Research on Cancer. Vitamin D and cancer. https://publications.iarc.fr/Book-And-Report-Series/Iarc-Working-Group-Reports/Vitamin-D-And-Cancer-2008 [Accessed April 2024]
NHS. Vitamin D. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/vitamins-and-minerals/vitamin-d/ [Accessed April 2024]
Last reviewed: 15 May 2024
Next due for review: 15 May 2027