Major errors like blade failures are incredibly rare, but — like the risk of whale injuries — are precisely the sort of negative externality activists have had a tendency of magnifying when fighting offshore wind. Should Trump win in November and retake the White House, he could indefinitely stall projects in the nascent sector across both coasts, as operations often fall under the scope of federal control.
“If Donald Trump is elected, he has said on Day 1 he would terminate offshore approvals. He has said he will do that, and frankly he generally keeps his word,” Bruce Afrin, an attorney representing activists challenging projects off the New Jersey coastline, told me. And while he sees Vineyard Wind becoming a focal point of that effort, he also told me, “I’m sure they’re going to take a broader approach.”
Nearly all offshore wind projects have to face at least some form of federal review. Projects at commercial scale will usually be in federal waters — more than 3 miles from a state’s coastline — because the best wind is further from shore; in addition, permits may be required on endangered species and water regulations to build turbines or construct cabling.
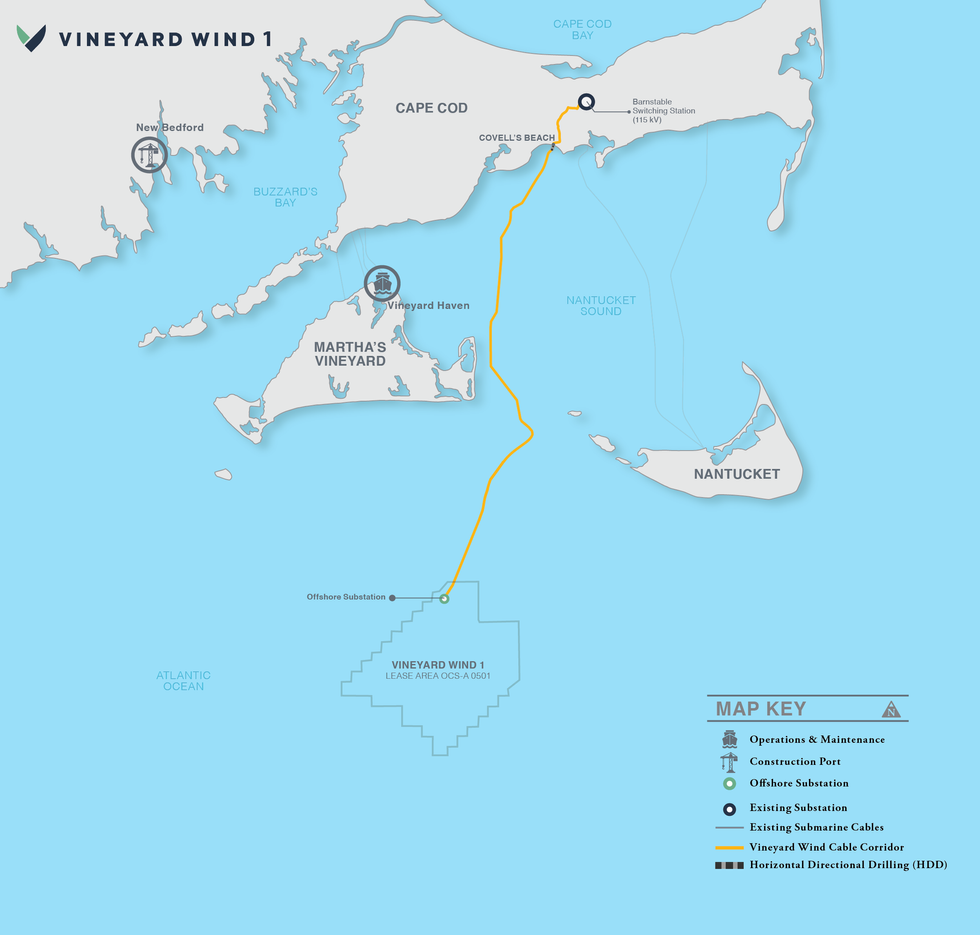
Very few existing offshore wind projects have been fully permitted and reached the construction phase. There’s Revolution, Sunrise, Coastal Virginia, and, of course, Vineyard Wind, which is now in a work stoppage following the blade failure. Many other projects are still in the permitting process, per K&L Gates attorney Theodore Paradise, who advises project developers in the sector. Paradise told me data on how many projects are in the federal regulatory pipeline is scattered across various federal sources, making it “kind of an IKEA situation.”
Given how few projects have received all of their permits to date, this is a worrisome hypothetical to climate advocates and professionals working in offshore wind.
“Any project going through any of those gauntlets may be dead on arrival,” attorney Jeff Thaler, who consults on offshore and onshore wind projects, told me. “That’s the uncertainty and concern, and investors do not like uncertainty like that.”
Nothing is certain
Both Thaler and Paradise said regulators already take the risk of blade failures and a multitude of other potential project risks seriously. (This is why, for example, there are boat speed restrictions near offshore wind projects.) Not to mention that wind turbines are not a new technology and have been operating in much larger numbers offshore in Europe and China without much incident.
Those few projects in construction still face legal challenges. Coastal Virginia, for example, was allowed to continue construction despite a lawsuit from conservative legal groups over the risks posed to endangered whales. If re-elected, Trump and his Justice Department would have the opportunity to stop defending the government’s approvals of the project and side with the legal challengers.
Whether it would be possible for Trump to undo previously issued approvals is a thornier question. Afrin argued that a Trump administration both could and would re-examine previous approvals related to offshore wind projects, under the justification that the government erroneously issued them or failed to properly conduct a specific analysis. Existing environmental laws like the National Environmental Policy Act, Afrin said, give ���enormous tools” to “those who organize and have standing” in litigation.
Paradise made an audible sigh when I asked whether a future Trump administration could feasibly go that far.
“Some folks you’ll talk to might say, oh [they have] approved it, we’re all set,” he said. “If the administration were to change, you can imagine a scenario where somebody sues on an issued permit and the Justice Department decides not to defend the agency action, or maybe they want to settle with the folks bringing the suit.”
Some permits may be impossible to undo because project developers have a vested right in a regulatory approval depending on how far along they are, Thaler said. But if construction has yet to begin and more permits are needed, a Trump administration could potentially have an opening.
The risk lies in what happens to public perception and political maneuvering. Thaler compared what’s happening with Vineyard Wind to the PR backlash against Boeing after a door came out of a plane in the middle of a flight. “Any time this gets attention it will have an impact. People will be raising more concerns. Those who have been opposing will be emboldened, or energized, no pun intended.” That said, after the door debacle, “People kept flying,” Thaler said. “There was a suspension of that particular jet type for a while, but then people resumed flying around the world.”
Hope against a future
Scrutinizing offshore wind tech is already on the table to some in the Trumpworld braintrust. Oliver McPherson-Smith, head of energy and environment issues for the America First Policy Institute, told Axios last year that he wants regulators in a future administration to look “very, very closely at the environmental effects of all new technologies, including offshore wind.” Advocates fighting offshore wind certainly feel emboldened by the Vineyard Wind blade failure and are looking to magnify the importance of its environmental impacts. Mandy Gunasekara — the author of Project 2025’s section on dismantling the Environmental Protection Agency — on Monday retweeted claims that the failure was a “disaster” that environmentalists were “downplaying.”
Later this week, representatives from Vineyard Wind will appear in court to defend against a lawsuit from the conservative Texas Public Policy Foundation, seeking to stop the project on behalf of people in the commercial fishing industry. The group cited the blade failure in a press release about the case: “The federal government is required to ensure safety and environmental protection by law when approving projects like this — and they knew this project had environmental risks like the one that came to pass here — but they let it happen anyway.”
Some offshore wind industry backers are optimistic about the ability for the industry to weather the storm of a future Trump administration, however. Sam Salustro, vice president of strategic communication for Oceantic, formerly known as the Business Network for Offshore Wind, told me that he thinks it’s not a done deal Trump puts the breaks on offshore wind permits given the “enormous amount of investment and job creation that is happening from this dependable pipeline of projects coming through.”
He also pointed to examples of Republican support from folks like Virginia Gov. Glenn Youngkin and House Majority Leader Steve Scalise, who recently attended the christening of a new port in his state of Louisiana that will serve the offshore wind industry. “This is an industry that has robust bipartisan support from the people who know it best,” he said.
When asked specifically about how the Vineyard Wind blade failure would impact the future of U.S. industry growth, Salustro told me he didn’t immediately know how to respond. Ultimately, he settled on a brighter outlook. “We still have three other projects that are continuing development. This is a safety issue that is going to be addressed. From global data, we understand how rare it is, so I don’t see it as a huge hiccup to the industry like inflation was. Probably limited impact.”
Dave Rogers of Sierra Club, meanwhile, acknowledged that while the Vineyard Wind situation is “not great,” there is “a long track record we can point to” on project efficacy and environmental safety. While its critical regulators and companies figure out what went awry here, “it’s critical that it doesn’t actually slow down the deployment of offshore wind.”
“It’s not necessarily our job to get out ahead of [this],” Rogers said, “but we do think it’s important this is contextualized on a global scale so that people understand how rare something like this is and that offshore wind is going to be a key part of a decarbonization strategy in the U.S.”








 Rhodium Group
Rhodium Group Google
Google