Intel Aggressively Dropping Power Consumption in Future Notebook Processors

During Intel's annual investor relations event earlier this week, Intel outlined a fundamental shift in its future processor designs that will likely impact Apple's future notebooks.
Until now, the bulk of Intel's notebook chips are design to draw around 35 watts of power--many of its notebook parts are lower, and some are higher, but 35 watts is the center point for Intel's portable lines. Going forward, however, the new center point will be in the 10 to 15 watt range.
Intel's future roadmap for notebook processors will now target a much lower power draw then present chips. That means ultra-low voltage processors like those found in the MacBook Air will become the norm instead of a specialty product.

Intel seems to be clearly feeling the pressure of the growing smartphone and tablet market, According to the Financial Times, Otellini describes a future of PCs evolving into "higher performance mainstream-priced, touch-enabled device that would not compromise on features such as thinness, instant-on capabilities, permanent internet connectivity and all-day battery life." Apple's notebook line will certainly benefit from these advances.
Intel and Apple have had a close relationship since Apple switched over to Intel's processors several years ago. Apple has frequently been the first computer manufacturer to ship the latest Intel technologies. In a Reuters report yesterday, Intel said they work very closely with Apple and that Apple even influences their roadmap:
"We work very closely with them and we're constantly looking down the road at what we can be doing relative to future products. I'd go as far as to say Apple helps shape our roadmap," Kilroy said.
Popular Stories
Apple will adopt the same rear chassis manufacturing process for the iPhone SE 4 that it is using for the upcoming standard iPhone 16, claims a new rumor coming out of China. According to the Weibo-based leaker "Fixed Focus Digital," the backplate manufacturing process for the iPhone SE 4 is "exactly the same" as the standard model in Apple's upcoming iPhone 16 lineup, which is expected to...
Apple typically releases its new iPhone series around mid-September, which means we are about two months out from the launch of the iPhone 16. Like the iPhone 15 series, this year's lineup is expected to stick with four models – iPhone 16, iPhone 16 Plus, iPhone 16 Pro, and iPhone 16 Pro Max – although there are plenty of design differences and new features to take into account. To bring ...
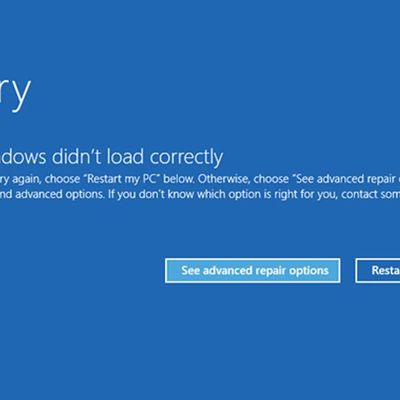
A widespread system failure is currently affecting numerous Windows devices globally, causing critical boot failures across various industries, including banks, rail networks, airlines, retailers, broadcasters, healthcare, and many more sectors. The issue, manifesting as a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD), is preventing computers from starting up properly and forcing them into continuous recovery...
Israel-based mobile forensics company Cellebrite is unable to unlock iPhones running iOS 17.4 or later, according to leaked documents verified by 404 Media. The documents provide a rare glimpse into the capabilities of the company's mobile forensics tools and highlight the ongoing security improvements in Apple's latest devices. The leaked "Cellebrite iOS Support Matrix" obtained by 404 Media...
Apple is seemingly planning a rework of the Apple Watch lineup for 2024, according to a range of reports from over the past year. Here's everything we know so far. Apple is expected to continue to offer three different Apple Watch models in five casing sizes, but the various display sizes will allegedly grow by up to 12% and the casings will get taller. Based on all of the latest rumors,...
If you have an old Apple Watch and you're not sure what to do with it, a new product called TinyPod might be the answer. Priced at $79, the TinyPod is a silicone case with a built-in scroll wheel that houses the Apple Watch chassis. When an Apple Watch is placed inside the TinyPod, the click wheel on the case is able to be used to scroll through the Apple Watch interface. The feature works...