Dosing & Uses
Dosage Forms & Strengths
tablet, immediate-release
- 500mg (generic)
- 850mg (generic)
- 1000mg (generic)
tablet, extended-release
- 500mg (generic, Glumetza)
- 750mg (generic)
1000mg (generic, Glumetza)
oral solution
- 100mg/mL (Riomet)
oral suspension, extended-release
- 47.31g/473mL per bottle (Riomet ER)
- Reconstituted suspension is 500mg/5mL
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Adjunctive therapy to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes
Monotherapy or with sulfonylurea
Immediate-release tablet or solution
- Initial: 500 mg PO q12hr or 850 mg PO qDay with meals; increase dose in increments of 500 mg/week or 850 mg q2Weeks on the basis of glycemic control and tolerability
- Maintenance: 1500-2550 mg/day PO divided q8-12hr with meal
- Not to exceed 2550 mg/day
Extended-release tablet or suspension
- 500 mg PO qDay with dinner; titrate by 500 mg/day qWeek; not to exceed 2000 mg/day
Type 2 Diabetes Prevention (Off-label)
850 mg PO qDay
Target dosing: 850 mg PO q12hr
Dosage Modifications
Hepatic impairment: Avoid use; risk of lactic acidosis
Renal impairment
- Obtain eGFR before starting metformin
- eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m²: Contraindicated
- eGFR 30-45 mL/min/1.73 m²: Not recommended to initiate treatment
- Monitor eGFR at least annually or more often for those at risk for renal impairment (eg, elderly)
- If eGFR falls below 45mL/min/1.73 m² while taking metformin, risks and benefits of continuing therapy should be evaluated
- If eGFR falls below 30 mL/min/1.73 m² while taking metformin, discontinue drug
Discontinuation for iodinated contrast imaging procedures
- Discontinue metformin HCl at the time of, or prior to, an iodinated contrast imaging procedure in patients with an eGFR between 30 and 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 ; in patients with a history of liver disease, alcoholism, or heart failure; or in patients who will be administered intra-arterial iodinated contrast
- Re-evaluate eGFR 48 hr after imaging procedure; restart metformin HCl if renal function is stable
Dosing Consideration
Switching from metformin immediate-release to metformin extended-release
- Patients receiving metformin HCl may be switched to metformin extended-release at the same total daily dose, up to 2,000 mg/day
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (Orphan)
Orphan designation for treatment of pediatric polycystic ovary syndrome
Sponsor
- EffRx Pharmaceuticals SA; Wolleraustrass 41 B; 8807 Freienbach (SZ); SWITZERLAND
Myoclonus Epilepsy (Orphan)
Orphan designation for treatment of progressive myoclonus epilepsy type 2 (Lafora disease)
Sponsor
- Consorcio Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red, M.P. (CIBER); Monforte de Lemos, 3-5 Pabellon 11; Madrid, Spain
Dosage Forms & Strengths
tablet, immediate-release
- 500mg (generic)
- 850mg (generic)
- 1000mg (generic)
oral solution
- 100mg/mL (Riomet)
oral suspension, extended-release
- 47.31g/473mL per bottle (Riomet ER)
- Reconstituted suspension is 500mg/5mL
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults and pediatric patients (≥10 years) with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
10 to <17 years
-
Immediate-release
- Initial: 500 mg PO q12hr
- Maintenance: Titrate qWeek by 500 mg; no more than 2000 mg/day in divided doses
-
Extended-release
- 500 mg PO qDay with dinner; increase the dose in increments of 500 mg (5 mL) weekly, up to a maximum dose of 2,000 mg (20 mL) once daily, with the evening meal
Dosage Modifications
Renal impairment
- Obtain eGFR before initiating metformin
- eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m²: Contraindicated
- eGFR 30-45 mL/min/1.73 m²: Initiating not recommended
- Obtain GFR at least annually in all patients taking metformin; assess eGFR more frequently in patients at increased risk for renal impairment (eg, elderly)
- If eGFR falls to <45 mL/min/1.73 m² during treatment: Assess the benefits and risks of continuing treatment
- If eGFR falls to <30 mL/min/1.73 m² during treatment: Discontinue
Elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function; contraindicated in patients with renal impairment, carefully monitor renal function in the elderly and use with caution as age increases
Not for use in patients >80 years unless normal renal function establishedInitial and maintenance dosing of metformin should be conservative in patients with advanced age due to the potential for decreased renal function in this population
Controlled clinical studies of metformin did not include sufficient numbers of elderly patients to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients
Interactions
Interaction Checker
No Results

Contraindicated
Serious - Use Alternative
Significant - Monitor Closely
Minor

Contraindicated (0)
Serious - Use Alternative (13)
- contrast media (iodinated)
contrast media (iodinated) increases levels of metformin by decreasing renal clearance. Contraindicated. Acute renal failure or lactic acidosis may result. D/c metformin 48 hr before and after imaging study.
- ethanol
ethanol increases toxicity of metformin by Other (see comment). Contraindicated. Comment: Excessive EtOH consumption may alter glycemic control. Some sulfonylureas may produce a disulfiram like rxn; alcohol may potentiate the risk of lactic acidosis.
- ioversol
ioversol increases levels of metformin by decreasing renal clearance. Contraindicated. Acute renal failure or lactic acidosis may result. D/c metformin 48 hr before and after imaging study.
- methylene blue
methylene blue will increase the level or effect of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pacritinib
pacritinib will increase the level or effect of metformin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant administration of pacritinib (OCT1 inhibitor) with OCT1 substrates may increase the plasma concentrations of these substrates.
- ranolazine
ranolazine will increase the level or effect of metformin by decreasing elimination. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Limit metformin dose to 1700 mg/day when used together with ranolazine 1000 mg twice daily; monitor closelly for signs or symptoms of metformin toxicity
- risdiplam
risdiplam will increase the level or effect of metformin by decreasing elimination. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Risdiplam inhibits MATE1 and MATE2-K. If unable to avoid coadministration with MATE substrates, consider dosage reduction of MATE substrate.
- selegiline
selegiline will increase the level or effect of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- selegiline transdermal
selegiline transdermal will increase the level or effect of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tafenoquine
tafenoquine will increase the level or effect of metformin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Tafenoquine inhibits organic cation transporter-2 (OCT2) and multidrug and toxin extrusion (MATE) transporters in vitro. Avoid coadministration with OCT2 or MATE substrates. If coadministration cannot be avoided, monitor for substrate-related toxicities and consider dosage reduction if needed based on product labeling of the coadministered drug.
- tedizolid
tedizolid will increase the level or effect of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tranylcypromine
tranylcypromine will increase the level or effect of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- trilaciclib
trilaciclib will decrease the level or effect of metformin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of trilaciclib (OCT2, MATE1, and MATE-2K inhibitor) with substrates where minimal increased concentration in kidney or blood may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicities.
Monitor Closely (198)
- acetazolamide
acetazolamide increases toxicity of metformin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Decreases serum bicarbonate and induce non-anion gap, hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis.
- albiglutide
albiglutide, metformin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concurrent use may increase risk of hypoglycemia; monitor glucose levels.
- amiodarone
amiodarone will increase the level or effect of metformin by basic (cationic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Use Caution/Monitor.
- amlodipine
amlodipine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- aripiprazole
aripiprazole, metformin. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Atypical antipsychotics have been associated with hyperglycemia that may alter blood glucose control; monitor glucose levels closely.
- asenapine
asenapine, metformin. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Atypical antipsychotics have been associated with hyperglycemia that may alter blood glucose control; monitor glucose levels closely.
- atazanavir
atazanavir decreases effects of metformin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Reports of hyperglycemia due to insulin resistance with protease inhibitors. .
- benazepril
benazepril increases toxicity of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increases risk for hypoglycemia and lactic acidosis.
- benzphetamine
benzphetamine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- betamethasone
betamethasone decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- bictegravir
bictegravir will increase the level or effect of metformin by decreasing renal clearance. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Bictegravir inhibits organic cation transporter 2 (OCT2) and multidrug and toxin extrusion transporter 1 (MATE1) in vitro. Coadministration with OCT2 and MATE1 substrates may increase their plasma concentrations. Metformin dose reduction may be required.
- bitter melon
bitter melon increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypoglycemia.
- brexpiprazole
brexpiprazole decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- bumetanide
bumetanide decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- bupropion
bupropion increases levels of metformin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Bupropion may inhibit OCT2 mediated renal excretion of metformin.
- captopril
captopril increases toxicity of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increases risk for hypoglycemia and lactic acidosis.
- cariprazine
cariprazine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cephalexin
cephalexin increases toxicity of metformin by decreasing renal clearance. Use Caution/Monitor. particularly in patients who may have other risk factors for metformin toxicity. .
- ceritinib
ceritinib decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- chlorpromazine
chlorpromazine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- cimetidine
cimetidine will increase the level or effect of metformin by basic (cationic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cinnamon
cinnamon increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Potential for hypoglycemia.
- ciprofloxacin
ciprofloxacin increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hyper and hypoglycemia have been reported in patients treated concomitantly with quinolones and antidiabetic agents. Careful monitoring of blood glucose is recommended.
- citalopram
citalopram increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- clevidipine
clevidipine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- clozapine
clozapine, metformin. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Atypical antipsychotics have been associated with hyperglycemia that may alter blood glucose control; monitor glucose levels closely.
- colesevelam
colesevelam increases levels of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- conjugated estrogens
conjugated estrogens decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- corticotropin
corticotropin decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dabrafenib
dabrafenib decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dalfampridine
metformin, dalfampridine. Either increases levels of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Metformin and dalfampridine are organic cation transporter 2 (OCT2) substrates; both drugs may compete for renal tubular uptake and could potentially increase systemic exposure of either drug when administered concomitantly.
- darunavir
darunavir decreases effects of metformin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Reports of hyperglycemia due to insulin resistance with protease inhibitors. .
- desogestrel
desogestrel decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- diatrizoate
diatrizoate increases toxicity of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Administration of intravascular iodinated contrast agents in metformin-treated patients has led to rare cases of acute decrease in renal function and the occurrence of lactic acidosis. The American College of Radiology Guidelines (2018) recommend temporarily stopping metformin in patients with eGFR is <30 mL/min/1.73 m2 or who are undergoing arterial catheter studies that might result in emboli to the renal arteries. Continue to withhold metformin for 48 hr subsequent to the procedure and reinstituted only after renal function has been reevaluated and found to be normal. .
- diatrizoate meglumine/diatrizoate sodium
diatrizoate meglumine/diatrizoate sodium increases toxicity of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Administration of intravascular iodinated contrast agents in metformin-treated patients has led to rare cases of acute decrease in renal function and the occurrence of lactic acidosis. The American College of Radiology Guidelines (2018) recommend temporarily stopping metformin in patients with eGFR is <30 mL/min/1.73 m2 or who are undergoing arterial catheter studies that might result in emboli to the renal arteries. Continue to withhold metformin for 48 hr subsequent to the procedure and reinstituted only after renal function has been reevaluated and found to be normal. .
- diazoxide
diazoxide decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dichlorphenamide
dichlorphenamide, metformin. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Both drugs can cause metabolic acidosis.
- dienogest/estradiol valerate
dienogest/estradiol valerate decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- diethylpropion
diethylpropion decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- digoxin
digoxin, metformin. Either increases levels of the other by basic (cationic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Use Caution/Monitor. Measure serum digoxin concentrations before initiating metformin. Monitor patients who take both metformin and digoxin for possible digoxin toxicity and lactic acidosis. Reduce the digoxin and/or metformin dose as necessary.
- diltiazem
diltiazem decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- dofetilide
dofetilide will increase the level or effect of metformin by basic (cationic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dolutegravir
dolutegravir will increase the level or effect of metformin by decreasing renal clearance. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Dolutegravir inhibits the renal organic cation transporter, OCT2; when used with metformin, limit total daily dose of metformin to 1,000 mg either when starting metformin or dolutegravir; when stopping dolutegravir, adjustment of metformin dose may be necessary; monitor blood glucose when initiating concomitant use and after withdrawal of dolutegravir
- drospirenone
drospirenone decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dulaglutide
dulaglutide, metformin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents.
- enalapril
enalapril increases toxicity of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increases risk for hypoglycemia and lactic acidosis.
- entecavir
entecavir, metformin. Either increases levels of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Coadministration of entecavir with metformin may increase the risk of lactic acidosis.
- erdafitinib
metformin increases levels of erdafitinib by decreasing renal clearance. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider alternatives that are not OCT2 substrates or consider reducing the dose of OCT2 substrates based on tolerability.
- escitalopram
escitalopram increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- estradiol
estradiol decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- estrogens conjugated synthetic
estrogens conjugated synthetic decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- estropipate
estropipate decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ethacrynic acid
ethacrynic acid decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ethinylestradiol
ethinylestradiol decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ethiodized oil
ethiodized oil increases toxicity of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Administration of intravascular iodinated contrast agents in metformin-treated patients has led to rare cases of acute decrease in renal function and the occurrence of lactic acidosis. The American College of Radiology Guidelines (2018) recommend temporarily stopping metformin in patients with eGFR is <30 mL/min/1.73 m2 or who are undergoing arterial catheter studies that might result in emboli to the renal arteries. Continue to withhold metformin for 48 hr subsequent to the procedure and reinstituted only after renal function has been reevaluated and found to be normal. .
- etonogestrel
etonogestrel decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- everolimus
everolimus decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- exenatide injectable solution
exenatide injectable solution, metformin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concurrent use may increase risk of hypoglycemia; monitor glucose levels.
- exenatide injectable suspension
exenatide injectable suspension, metformin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concurrent use may increase risk of hypoglycemia; monitor glucose levels.
- felodipine
felodipine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- fleroxacin
fleroxacin increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Quinolone antibiotic administration may result in hyper- or hypoglycemia. Gatifloxacin is most likely to produce dysglycemia; moxifloxacin is least likely.
- fluoxetine
fluoxetine increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fluphenazine
fluphenazine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- fluvoxamine
fluvoxamine increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fosamprenavir
fosamprenavir decreases effects of metformin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Reports of hyperglycemia due to insulin resistance with protease inhibitors. .
- fosinopril
fosinopril increases toxicity of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increases risk for hypoglycemia and lactic acidosis.
- fosphenytoin
fosphenytoin decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- gemifloxacin
gemifloxacin increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Quinolone antibiotic administration may result in hyper- or hypoglycemia. Gatifloxacin is most likely to produce dysglycemia; moxifloxacin is least likely.
- givinostat
givinostat will increase the level or effect of metformin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Givinostat is a weak OAT2 inhibitor. Closely monitor if coadministered with orally administered OCT2 sensitive substrates for which a small change in substrate plasma concentration may lead to serious toxicities.
- glucagon intranasal
glucagon intranasal decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- glycopyrrolate
glycopyrrolate increases toxicity of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. May require a dose reduction.
- goserelin
goserelin decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- histrelin
histrelin decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- hydroxyprogesterone caproate (DSC)
hydroxyprogesterone caproate (DSC) decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- iloperidone
iloperidone, metformin. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Atypical antipsychotics have been associated with hyperglycemia that may alter blood glucose control; monitor glucose levels closely.
- imidapril
imidapril increases toxicity of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increases risk for hypoglycemia and lactic acidosis.
- indinavir
indinavir decreases effects of metformin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Reports of hyperglycemia due to insulin resistance with protease inhibitors. .
- insulin aspart
metformin, insulin aspart. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents.
- insulin aspart protamine/insulin aspart
metformin, insulin aspart protamine/insulin aspart. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents.
- insulin degludec
metformin, insulin degludec. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents.
- insulin degludec/insulin aspart
metformin, insulin degludec/insulin aspart. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents.
- insulin detemir
metformin, insulin detemir. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents.
- insulin glargine
metformin, insulin glargine. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents.
- insulin glulisine
metformin, insulin glulisine. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents.
- insulin inhaled
metformin, insulin inhaled. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents.
- insulin isophane human/insulin regular human
metformin, insulin isophane human/insulin regular human. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents.
- insulin lispro
metformin, insulin lispro. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents.
- insulin lispro protamine/insulin lispro
metformin, insulin lispro protamine/insulin lispro. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents.
- insulin NPH
metformin, insulin NPH. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents.
- insulin regular human
metformin, insulin regular human. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents.
- iodixanol
iodixanol increases toxicity of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Administration of intravascular iodinated contrast agents in metformin-treated patients has led to rare cases of acute decrease in renal function and the occurrence of lactic acidosis. The American College of Radiology Guidelines (2018) recommend temporarily stopping metformin in patients with eGFR is <30 mL/min/1.73 m2 or who are undergoing arterial catheter studies that might result in emboli to the renal arteries. Continue to withhold metformin for 48 hr subsequent to the procedure and reinstituted only after renal function has been reevaluated and found to be normal. .
- ioflupane I 123
ioflupane I 123 increases toxicity of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Administration of intravascular iodinated contrast agents in metformin-treated patients has led to rare cases of acute decrease in renal function and the occurrence of lactic acidosis. The American College of Radiology Guidelines (2018) recommend temporarily stopping metformin in patients with eGFR is <30 mL/min/1.73 m2 or who are undergoing arterial catheter studies that might result in emboli to the renal arteries. Continue to withhold metformin for 48 hr subsequent to the procedure and reinstituted only after renal function has been reevaluated and found to be normal. .
- iohexol
iohexol increases toxicity of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Administration of intravascular iodinated contrast agents in metformin-treated patients has led to rare cases of acute decrease in renal function and the occurrence of lactic acidosis. The American College of Radiology Guidelines (2018) recommend temporarily stopping metformin in patients with eGFR is <30 mL/min/1.73 m2 or who are undergoing arterial catheter studies that might result in emboli to the renal arteries. Continue to withhold metformin for 48 hr subsequent to the procedure and reinstituted only after renal function has been reevaluated and found to be normal. .
- iopamidol
iopamidol increases toxicity of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Administration of intravascular iodinated contrast agents in metformin-treated patients has led to rare cases of acute decrease in renal function and the occurrence of lactic acidosis. The American College of Radiology Guidelines (2018) recommend temporarily stopping metformin in patients with eGFR is <30 mL/min/1.73 m2 or who are undergoing arterial catheter studies that might result in emboli to the renal arteries. Continue to withhold metformin for 48 hr subsequent to the procedure and reinstituted only after renal function has been reevaluated and found to be normal. .
- iopromide
iopromide increases toxicity of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Administration of intravascular iodinated contrast agents in metformin-treated patients has led to rare cases of acute decrease in renal function and the occurrence of lactic acidosis. The American College of Radiology Guidelines (2018) recommend temporarily stopping metformin in patients with eGFR is <30 mL/min/1.73 m2 or who are undergoing arterial catheter studies that might result in emboli to the renal arteries. Continue to withhold metformin for 48 hr subsequent to the procedure and reinstituted only after renal function has been reevaluated and found to be normal. .
- ioversol
ioversol increases toxicity of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Administration of intravascular iodinated contrast agents in metformin-treated patients has led to rare cases of acute decrease in renal function and the occurrence of lactic acidosis. The American College of Radiology Guidelines (2018) recommend temporarily stopping metformin in patients with eGFR is <30 mL/min/1.73 m2 or who are undergoing arterial catheter studies that might result in emboli to the renal arteries. Continue to withhold metformin for 48 hr subsequent to the procedure and reinstituted only after renal function has been reevaluated and found to be normal. .
- ioxilan
ioxilan increases toxicity of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Administration of intravascular iodinated contrast agents in metformin-treated patients has led to rare cases of acute decrease in renal function and the occurrence of lactic acidosis. The American College of Radiology Guidelines (2018) recommend temporarily stopping metformin in patients with eGFR is <30 mL/min/1.73 m2 or who are undergoing arterial catheter studies that might result in emboli to the renal arteries. Continue to withhold metformin for 48 hr subsequent to the procedure and reinstituted only after renal function has been reevaluated and found to be normal. .
- isocarboxazid
isocarboxazid will increase the level or effect of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- isoniazid
isoniazid decreases effects of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- isradipine
isradipine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- ketotifen, ophthalmic
ketotifen, ophthalmic, metformin. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Combination may result in thrombocytopenia (rare). Monitor CBC.
- lanreotide
lanreotide decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- leuprolide
leuprolide decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- levofloxacin
levofloxacin increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Quinolone antibiotic administration may result in hyper- or hypoglycemia. Gatifloxacin is most likely to produce dysglycemia; moxifloxacin is least likely.
- levonorgestrel intrauterine
levonorgestrel intrauterine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- levonorgestrel oral
levonorgestrel oral decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- levothyroxine
levothyroxine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- linezolid
linezolid will increase the level or effect of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- liothyronine
liothyronine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- liotrix
liotrix decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- liraglutide
liraglutide, metformin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concurrent use may increase risk of hypoglycemia; monitor glucose levels.
- lisinopril
lisinopril increases toxicity of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increases risk for hypoglycemia and lactic acidosis.
- lithium
metformin decreases levels of lithium by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: SGLT2 inhibitors with lithium may decrease serum lithium concentrations; monitor serum lithium concentration more frequently during therapy initiation and dosage changes.
- lonapegsomatropin
lonapegsomatropin decreases effects of metformin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Closely monitor blood glucose when treated with antidiabetic agents. Lonapegsomatropin may decrease insulin sensitivity, particularly at higher doses. Patients with diabetes mellitus may require adjustment of their doses of insulin and/or other antihyperglycemic agents.
lonapegsomatropin decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Growth hormone (GH) analogs may decrease insulin sensitivity, particularly at higher doses. Antidiabetic agents may require dose adjustment after initiating growth hormone. - lopinavir
lopinavir decreases effects of metformin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Reports of hyperglycemia due to insulin resistance with protease inhibitors. .
- lurasidone
lurasidone, metformin. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Atypical antipsychotics have been associated with hyperglycemia that may alter blood glucose control; monitor glucose levels closely.
- marijuana
marijuana decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- mavorixafor
mavorixafor will decrease the level or effect of metformin by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor for glycemic control and adjust metformin dose if needed.
- mecasermin
mecasermin increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Additive hypoglycemic effects.
- medroxyprogesterone
medroxyprogesterone decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- methamphetamine
methamphetamine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- methazolamide
methazolamide increases toxicity of metformin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Decreases serum bicarbonate and induce non-anion gap, hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis.
- moexipril
moexipril increases toxicity of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increases risk for hypoglycemia and lactic acidosis.
- moxifloxacin
moxifloxacin increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Quinolone antibiotic administration may result in hyper- or hypoglycemia. Gatifloxacin is most likely to produce dysglycemia; moxifloxacin is least likely.
- nelfinavir
nelfinavir decreases effects of metformin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Reports of hyperglycemia due to insulin resistance with protease inhibitors. .
- niacin
niacin decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- nicardipine
nicardipine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- nifedipine
nifedipine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- nilotinib
nilotinib decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nimodipine
nimodipine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- nisoldipine
nisoldipine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- nizatidine
nizatidine will increase the level or effect of metformin by decreasing renal clearance. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- norelgestromin
norelgestromin decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- norethindrone
norethindrone decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- norgestimate
norgestimate decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- octreotide
octreotide decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ofloxacin
ofloxacin increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Quinolone antibiotic administration may result in hyper- or hypoglycemia. Gatifloxacin is most likely to produce dysglycemia; moxifloxacin is least likely.
- olanzapine
olanzapine, metformin. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Atypical antipsychotics have been associated with hyperglycemia that may alter blood glucose control; monitor glucose levels closely.
- omacetaxine
omacetaxine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir & dasabuvir (DSC)
ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir & dasabuvir (DSC) increases toxicity of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor for signs of onset of lactic acidosis such as respiratory distress, somnolence, and non-specific abdominal distress or worsening renal function; concomitant metformin use in patients with renal insufficiency or hepatic impairment not recommended.
- ondansetron
ondansetron increases levels of metformin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Ondansetron inhibition of transporters (MATE or OCTs), which are responsible for active renal secretion of metformin may play a role.
- opuntia ficus indica
opuntia ficus indica increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- paliperidone
paliperidone, metformin. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Atypical antipsychotics have been associated with hyperglycemia that may alter blood glucose control; monitor glucose levels closely.
- paroxetine
paroxetine increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- pasireotide
pasireotide decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- patiromer
patiromer will decrease the level or effect of metformin by drug binding in GI tract. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Separate administration by at least 3 hr from patiromer
- pentamidine
pentamidine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- perindopril
perindopril increases toxicity of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increases risk for hypoglycemia and lactic acidosis.
- perphenazine
perphenazine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- phendimetrazine
phendimetrazine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- phenelzine
phenelzine will increase the level or effect of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- phentermine
phentermine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- phenytoin
phenytoin decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- procainamide
metformin will increase the level or effect of procainamide by basic (cationic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Use Caution/Monitor.
- procarbazine
procarbazine will increase the level or effect of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- prochlorperazine
prochlorperazine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- progesterone intravaginal gel
progesterone intravaginal gel decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- progesterone micronized
progesterone micronized decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- progesterone, natural
progesterone, natural decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- promethazine
promethazine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- quetiapine
quetiapine, metformin. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Atypical antipsychotics have been associated with hyperglycemia that may alter blood glucose control; monitor glucose levels closely.
- quinapril
quinapril increases toxicity of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increases risk for hypoglycemia and lactic acidosis.
- quinidine
quinidine will increase the level or effect of metformin by basic (cationic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ramipril
ramipril increases toxicity of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increases risk for hypoglycemia and lactic acidosis.
- rasagiline
rasagiline will increase the level or effect of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- risperidone
risperidone, metformin. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Atypical antipsychotics have been associated with hyperglycemia that may alter blood glucose control; monitor glucose levels closely.
- ritonavir
ritonavir decreases effects of metformin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Reports of hyperglycemia due to insulin resistance with protease inhibitors. .
- saquinavir
saquinavir decreases effects of metformin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Reports of hyperglycemia due to insulin resistance with protease inhibitors. .
- sertraline
sertraline increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- shark cartilage
shark cartilage increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Theoretical interaction.
- sirolimus
sirolimus decreases levels of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- somapacitan
somapacitan decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Growth hormone (GH) analogs may decrease insulin sensitivity, particularly at higher doses. Antidiabetic agents may require dose adjustment after initiating growth hormone.
- somatrogon
somatrogon decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Growth hormone (GH) analogs may decrease insulin sensitivity, particularly at higher doses. Antidiabetic agents may require dose adjustment after initiating growth hormone.
- somatropin
somatropin decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Growth hormone (GH) analogs may decrease insulin sensitivity, particularly at higher doses. Antidiabetic agents may require dose adjustment after initiating growth hormone.
- sulfamethoxypyridazine
sulfamethoxypyridazine increases effects of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypoglycemia.
- tacrolimus
tacrolimus decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- temsirolimus
temsirolimus decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tenofovir DF
tenofovir DF increases levels of metformin by decreasing renal clearance. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of lactic acidosis.
- thioridazine
thioridazine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- thyroid desiccated
thyroid desiccated decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- tibolone
tibolone decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tipranavir
tipranavir decreases effects of metformin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Reports of hyperglycemia due to insulin resistance with protease inhibitors. .
- topiramate
topiramate increases toxicity of metformin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Decreases serum bicarbonate and induce non-anion gap, hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis.
- torsemide
torsemide decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- trandolapril
trandolapril increases toxicity of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increases risk for hypoglycemia and lactic acidosis.
- triamcinolone acetonide injectable suspension
triamcinolone acetonide injectable suspension decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Corticosteroids may diminish hypoglycemic effect of antidiabetic agents. Monitor blood glucose levels carefully.
- trifluoperazine
trifluoperazine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
- trimethoprim
trimethoprim increases levels of metformin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Trimethoprim may inhibit active renal tubular secretion of metformin (eg, via OCT2, MATE1); dose adjustments may be necessary.
- triptorelin
triptorelin decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- trospium chloride
metformin will decrease the level or effect of trospium chloride by increasing renal clearance. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration reduced steady state trospium systemic exposure (decreased AUC and Cmax) by competing for renal tubular secretion
- vandetanib
vandetanib increases levels of metformin by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Vandetanib inhibits the uptake of substrates of organic cation transporter type 2 (OCT2).
- verapamil
verapamil decreases effects of metformin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Verapamil may inhibit hepatic uptake of metformin by OCT1 and/or other transporters.
- vilazodone
vilazodone increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- vorinostat
vorinostat decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- vortioxetine
vortioxetine increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- xipamide
xipamide decreases levels of metformin by increasing renal clearance. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ziprasidone
ziprasidone, metformin. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Atypical antipsychotics have been associated with hyperglycemia that may alter blood glucose control; monitor glucose levels closely.
- zonisamide
zonisamide increases toxicity of metformin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Decreases serum bicarbonate and induce non-anion gap, hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis.
Minor (82)
- agrimony
agrimony increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- American ginseng
American ginseng increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- amitriptyline
amitriptyline increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- amoxapine
amoxapine increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- anamu
anamu increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Theoretical interaction.
- bendroflumethiazide
bendroflumethiazide decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Thiazide dosage >50 mg/day may increase blood glucose.
- budesonide
budesonide decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- chlorothiazide
chlorothiazide decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Thiazide dosage >50 mg/day may increase blood glucose.
- chlorthalidone
chlorthalidone decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Thiazide dosage >50 mg/day may increase blood glucose.
- chromium
chromium increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- clomipramine
clomipramine increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- clonidine
clonidine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Diminished symptoms of hypoglycemia.
clonidine, metformin. Other (see comment). Minor/Significance Unknown. Comment: Decreased symptoms of hypoglycemia. Mechanism: decreased hypoglycemia induced catecholamine production. - cornsilk
cornsilk increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Increased risk of hypoglycemia (theoretical interaction).
- cortisone
cortisone decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- cyanocobalamin
metformin decreases levels of cyanocobalamin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. It may take several years of metformin therapy to develop vitamin B12 deficiency.
- cyclopenthiazide
cyclopenthiazide decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Thiazide dosage >50 mg/day may increase blood glucose.
- damiana
damiana decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Theoretical interaction.
- danazol
danazol increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- deflazacort
deflazacort decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- desipramine
desipramine increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- devil's claw
devil's claw increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- dexamethasone
dexamethasone decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- diltiazem
diltiazem will increase the level or effect of metformin by basic (cationic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- doxepin
doxepin increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- elderberry
elderberry increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Increased risk of hypoglycemia (in vitro research).
- eucalyptus
eucalyptus increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Theoretical interaction.
- famotidine
famotidine increases levels of metformin by decreasing renal clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- fludrocortisone
fludrocortisone decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- fluoxymesterone
fluoxymesterone increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- fo-ti
fo-ti increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- folic acid
metformin decreases levels of folic acid by unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- forskolin
forskolin increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Colenol, a compound found in Coleus root, may stimulate insulin release.
- furosemide
metformin decreases levels of furosemide by unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
furosemide increases levels of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control; when drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia. - gotu kola
gotu kola increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. (Theoretical interaction).
- guanfacine
guanfacine decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Diminished symptoms of hypoglycemia.
guanfacine, metformin. Other (see comment). Minor/Significance Unknown. Comment: Decreased symptoms of hypoglycemia. Mechanism: decreased hypoglycemia induced catecholamine production. - gymnema
gymnema increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- horse chestnut seed
horse chestnut seed increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- hydrochlorothiazide
hydrochlorothiazide will increase the level or effect of metformin by basic (cationic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
hydrochlorothiazide decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Thiazide dosage >50 mg/day may increase blood glucose. - hydrocortisone
hydrocortisone decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ibuprofen/famotidine
ibuprofen/famotidine increases levels of metformin by decreasing renal clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- imipramine
imipramine increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- indapamide
indapamide decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Thiazide dosage >50 mg/day may increase blood glucose.
- juniper
juniper increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Increased risk of hypoglycemia (theoretical interaction).
- L-methylfolate
metformin decreases levels of L-methylfolate by unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- lofepramine
lofepramine increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- lycopus
lycopus increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Increased risk of hypoglycemia (theoretical interaction).
- maitake
maitake increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Increased risk of hypoglycemia (animal research).
- maprotiline
maprotiline increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- memantine
memantine will increase the level or effect of metformin by basic (cationic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- mesterolone
mesterolone increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- methyclothiazide
methyclothiazide will increase the level or effect of metformin by basic (cationic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
methyclothiazide decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Thiazide dosage >50 mg/day may increase blood glucose. - methylprednisolone
methylprednisolone decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- methyltestosterone
methyltestosterone increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- metolazone
metolazone decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Thiazide dosage >50 mg/day may increase blood glucose.
- midodrine
metformin will increase the level or effect of midodrine by basic (cationic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- nettle
nettle increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. (Theoretical interaction).
- nifedipine
nifedipine increases levels of metformin by enhancing GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- nortriptyline
nortriptyline increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ofloxacin
metformin will increase the level or effect of ofloxacin by basic (cationic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
ofloxacin, metformin. Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Potential dysglycemia. - oxandrolone
oxandrolone increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- oxymetholone
oxymetholone increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- pegvisomant
pegvisomant increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- potassium acid phosphate
potassium acid phosphate increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Interaction especially seen in the treatment of hypokalemia.
- potassium chloride
potassium chloride increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Interaction especially seen in the treatment of hypokalemia.
- potassium citrate
potassium citrate increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Interaction especially seen in the treatment of hypokalemia.
- prednisolone
prednisolone decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- prednisone
prednisone decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- protriptyline
protriptyline increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- quinine
metformin will increase the level or effect of quinine by basic (cationic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- sage
sage increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- stevia
stevia increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- sulfamethoxazole
sulfamethoxazole will increase the level or effect of metformin by basic (cationic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- testosterone
testosterone increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- testosterone buccal system
testosterone buccal system increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- testosterone topical
testosterone topical increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- tongkat ali
tongkat ali increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of hypoglycemia.
- trazodone
trazodone increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- triamterene
metformin will increase the level or effect of triamterene by basic (cationic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- trimethoprim
metformin will increase the level or effect of trimethoprim by basic (cationic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- trimipramine
trimipramine increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- vanadium
vanadium increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- verapamil
metformin will increase the level or effect of verapamil by basic (cationic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
Adverse Effects
>10%
Diarrhea, immediate-release product (53%)
Nausea/vomiting, immediate-release product (25%)
1-10%
Diarrhea, extended-release product (10%)
Nausea/vomiting, extended-release product (7%)
Low serum vitamin B-12 (7%)
Abdominal pain (1-5%)
Constipation (1-5%)
Abdomen distention (1-5%)
Dyspepsia/heartburn (1-5%)
Flatulence (1-5%)
Dizziness (1-5%)
Headache (1-5%)
Upper respiratory infection (1-5%)
Taste disturbance (1-5%)
Postmarketing Reports H3
Cholestatic, hepatocellular, and mixed hepatocellular liver injury
Frequency Not Defined
Lactic acidosis
Hypoglycemia
Warnings
Black Box Warnings
Lactic acidosis is a rare, but potentially severe, consequence of therapy with metformin; it is characterized by elevated blood lactate levels (>5 mmol/L), decreased blood pH, electrolyte disturbances with an increased anion gap, and an increased lactate/pyruvate ratio; when metformin is implicated as the cause of lactic acidosis, metformin plasma concentrations >5 mcg/mL are generally found
Risk factors for metformin-associated lactic acidosis include renal impairment, concomitant use of certain drugs (eg, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors such as topiramate), age 65 years old or greater, having a radiological study with contrast, surgery and other procedures, hypoxic states (e.g., acute congestive heart failure), excessive alcohol intake, and hepatic impairment; if metformin-associated lactic acidosis is suspected, immediately discontinue
Patients with CHF requiring pharmacologic management, in particular those with unstable or acute CHF who are at risk for hypoperfusion and hypoxemia, are at an increased risk for lactic acidosis; the risk for lactic acidosis increases with the degree of renal dysfunction and the patient’s age
Do not start in patients aged 80 years or older unless CrCl demonstrates that renal function is not reduced, because these patients are more susceptible to developing lactic acidosis; metformin should be promptly withheld in the presence of any condition associated with hypoxemia, dehydration, or sepsis
Should generally be avoided in patients with clinical or laboratory evidence of hepatic disease; patients should be cautioned against excessive alcohol intake, either acute or chronic, during metformin therapy because alcohol potentiates the effects of metformin on lactate metabolism
Discontinue metformin at the time of or before an iodinated contrast imaging procedure in patients with an eGFR between 30-60 mL/minute/1.73 m²; in patients with a history of liver disease, alcoholism, or heart failure; or in patients who will be administered intra-arterial iodinate contrast
The onset of lactic acidosis often is subtle and accompanied by nonspecific symptoms (eg, malaise, myalgias, respiratory distress, increasing somnolence, nonspecific abdominal distress); with marked acidosis, hypothermia, hypotension, and resistant bradyarrhythmias may occur; patients should be instructed regarding recognition of these symptoms and told to notify their physician immediately if the symptoms occur; metformin should be withdrawn until the situation is clarified; serum electrolytes, ketones, blood glucose, and, if indicated, blood pH, lactate levels, and even blood metformin levels may be useful
Once a patient is stabilized on any dose level of metformin, GI symptoms, which are common during initiation of therapy, are unlikely to be drug related; later occurrences of GI symptoms could be due to lactic acidosis or other serious disease
Lactic acidosis should be suspected in any diabetic patient with metabolic acidosis who is lacking evidence of ketoacidosis (ketonuria and ketonemia); lactic acidosis is a medical emergency that must be treated in a hospital setting; in a patient with lactic acidosis who is taking metformin, the drug should be discontinued immediately and general supportive care measures promptly instituted; metformin is highly dialyzable (clearance up to 170 mL/min under good hemodynamic conditions); prompt hemodialysis is recommended to correct the acidosis and to remove the accumulated metformin; such management often results in prompt reversal of symptoms and recovery
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to metformin
CHF
Diabetic ketoacidosis with or without coma
Severe renal disease: eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m²
Abnormal creatinine clearance resulting from shock, septicemia, or myocardial infarction
Lactation
Cautions
Increased risk of severe hypoglycemia especially in elderly, debilitated or malnourished, adrenal or pituitary insufficiency, dehydration, heavy alcohol use, hypoxic states, hepatic/renal impairment, stress due to infection, fever, trauma, or surgery
Concomitant administration of insulin and insulin secretagogues (e.g., sulfonylurea) may increase risk of hypoglycemia; therefore, a lower dose of insulin or insulin secretagogue may be required to minimize risk of hypoglycemia when used in combination with metformin
Withholding of food and fluids during surgical or other procedures may increase risk for volume depletion, hypotension, and renal impairment; therapy should be temporarily discontinued while patients have restricted food and fluid intake
Rare lactic acidosis may occur due to metformin accumulation; fatal in approximately 50% of cases; risk increases with age, degree of renal dysfunction, and with unstable or acute CHF; if metformin-associated lactic acidosis suspected, general supportive measures should be instituted promptly in a hospital setting, along with immediate discontinuation of therapy; in patients with a diagnosis or strong suspicion of lactic acidosis, prompt hemodialysis is recommended to correct acidosis and remove accumulated metformin (metformin hydrochloride is dialyzable, with a clearance of up to170 mL/minute under good hemodynamic conditions); hemodialysis has often resulted in reversal of symptoms and recovery
Possible increased risk of CV mortality
May cause ovulation in anovulatory and premenopausal PCOS patients
May be necessary to discontinue therapy with metformin and administer insulin if patient is exposed to stress (fever, trauma, infection), or experiences diabetic ketoacidosis
Several of the postmarketing cases of metformin-associated lactic acidosis occurred in setting of acute congestive heart failure (particularly when accompanied by hypoperfusion and hypoxemia); cardiovascular collapse (shock) acute myocardial infarction, sepsis, and other conditions associated with hypoxemia have been associated with lactic acidosis and may also cause prerenal azotemia; discontinue therapy when such events occur
May impair vitamin B12 or calcium intake/absorption; monitor B12 serum concentrations periodically with long-term therapy
Not indicated for use in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus that are insulin dependent due to lack of efficacy
Withhold in patients with dehydration and/or prerenal azotemia
Conclusive evidence of macrovascular risk reduction with metformin not established
Clinical recommendations based upon the patient’s renal function
- Before initiating therapy, obtain an eGFR
- Initiation of therapy is not recommended in patients with eGFR between 30 –45 mL/minute/1.73 m²
- Obtain an eGFR at least annually in all patients receiving therapy
- In patients at increased risk for development of renal impairment (e.g., the elderly), renal function should be assessed more frequently
- If eGFR later falls below 45 mL/minute/1.73 m², assess benefit and risk of continuing therapy
Iodinated contrast imaging procedures
- Discontinue metformin at the time of or before an iodinated contrast imaging procedure in patients with an eGFR between 30-60 mL/minute/1.73 m²; in patients with a history of liver disease, alcoholism, or heart failure; or in patients who will be administered intra-arterial iodinate contrast
- Reevaluate eGFR 48 hr after the imaging procedure; restart metformin if renal function is stable
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy
Limited data with in pregnant women are not sufficient to determine drug-associated risk for major birth defects or miscarriage; published studies with metformin use during pregnancy have not reported a clear association with metformin and major birth defect or miscarriage risk; poorly-controlled diabetes mellitus in pregnancy increases maternal risk for diabetic ketoacidosis, pre-eclampsia, spontaneous abortions, preterm delivery, stillbirth and delivery complications; poorly controlled diabetes mellitus increases the fetal risk for major birth defects, stillbirth, and macrosomia related morbidity
Human data
- Published data from post-marketing studies have not reported clear association with metformin and major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes when used during pregnancy; however, these studies cannot definitely establish absence of any metformin-associated risk because of methodological limitations, including small sample size and inconsistent comparator groups
Animal data
- Metformin hydrochloride did not adversely affect development outcomes when administered to pregnant rats and rabbits at doses up to 600 mg/kg/day; this represents exposure of about 2 and 5 times a 2550 mg clinical dose based on body surface area comparisons for rats and rabbits, respectively; determination of fetal concentrations demonstrated a partial placental barrier to metformin
Reproduction potential
- Discuss potential for unintended pregnancy with premenopausal women as therapy may result in ovulation in some anovulatory women
Lactation
Limited published studies report that metformin is present in human milk; however, there is insufficient information to determine effects of metformin on breastfed infant and no available information on effects of metformin on milk production; therefore, developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with mother’s clinical need for therapy and any potential adverse effects on breastfed child from therapy or from the underlying maternal condition
Pregnancy Categories
A: Generally acceptable. Controlled studies in pregnant women show no evidence of fetal risk.
B: May be acceptable. Either animal studies show no risk but human studies not available or animal studies showed minor risks and human studies done and showed no risk. C: Use with caution if benefits outweigh risks. Animal studies show risk and human studies not available or neither animal nor human studies done. D: Use in LIFE-THREATENING emergencies when no safer drug available. Positive evidence of human fetal risk. X: Do not use in pregnancy. Risks involved outweigh potential benefits. Safer alternatives exist. NA: Information not available.Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Decreases hepatic glucose production; decreases GI glucose absorption; increases target cell insulin sensitivity
Absorption
Bioavailability: 50-60%
Peak plasma time
- Regular-release: 2-3 hr
- Extended-release: 4-8 hr
Distribution
Protein bound: Minimal
Vd: 650 L (regular-release)
Metabolism
Metabolism: Not by liver
Elimination
Half-Life: 4-9 hr
Dialyzable: Yes (hemodialysis)
Renal clearance: 450-540 mL/min (regular-release)
Excretion: Urine (90%, by tubular secretion)
Administration
Oral Suspension Preparation (Riomet ER)
Remove bottle containing drug pellets and drug diluent bottle along with measuring cup from the box
Do not use if drug is expired, damaged, or defective
Pour contents of bottle containing drug pellets in to the drug diluent bottle and discard the empty pellet bottle
Shake bottle continuously in an up and down direction for at least 2 full min; reconstituted suspension is 500 mg/5 mL
Oral Administration
Take with an evening meal
Oral solution or suspension: Measure dose in the provided dosing cup
Extended-release tablets: Swallow tablets whole and never crush, cut, or chew
Missed dose
- Do not to take 2 doses the same day and to resume the usual dose with the next schedule dose
Storage
Tablets
- Store at 20-25ºC (68-77ºF); excursions permitted to 15-30ºC (59-86ºF)
Oral solution (Riomet)
- Store at 15-30ºC (59-86ºF)
Oral suspension (Riomet ER)
- Unused bottle: Store at 20-25ºC (68-77ºF)
- Reconstituted oral suspension: Store at 20-25°C (68-77ºF) for up to 100 days; do not repackage
Images
| BRAND | FORM. | UNIT PRICE | PILL IMAGE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Riomet oral - | 500 mg/5 mL solution |  | |
| Riomet oral - | 500 mg/5 mL solution |  | |
| Riomet oral - | 500 mg/5 mL solution |  | |
| Glumetza oral - | 1,000 mg tablet |  | |
| Glumetza oral - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 750 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet | 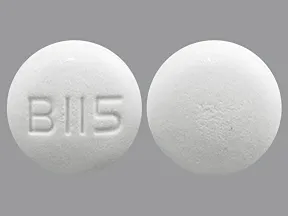 | |
| Metformin - | 1,000 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 750 mg tablet | 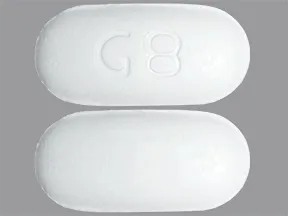 | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet | 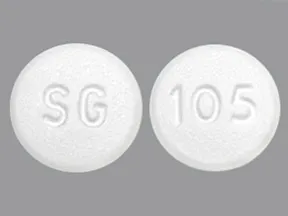 | |
| Metformin - | 850 mg tablet | 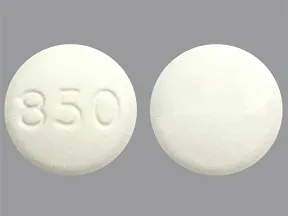 | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 850 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 1,000 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 1,000 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 850 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 1,000 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 750 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 1,000 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 1,000 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 750 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 750 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 850 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 1,000 mg tablet | 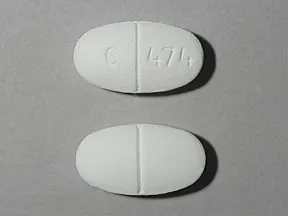 | |
| Metformin - | 625 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 850 mg tablet | 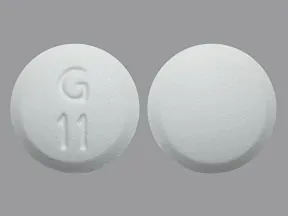 | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 850 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 850 mg tablet | 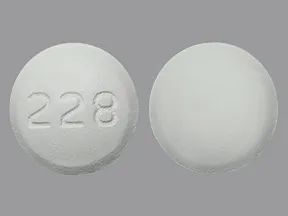 | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet | 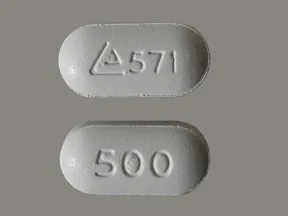 | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 1,000 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 750 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 1,000 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 850 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 1,000 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 1,000 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 1,000 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 1,000 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 1,000 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 1,000 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 750 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 1,000 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 1,000 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 1,000 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 1,000 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 750 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 1,000 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 1,000 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 750 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 750 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 1,000 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 750 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 1,000 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 850 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Metformin - | 1,000 mg tablet |  |
Copyright © 2010 First DataBank, Inc.
Patient Handout
Metformin
COMMON BRAND NAME(S): Fortamet, Glumetza
USES: What is metformin used for? Metformin is used to help lower blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes . Metformin may also be used for other conditions as determined by your healthcare provider. How does metformin work (mechanism of action)? Metformin works in a few different ways to help keep your blood glucose (sugar) from getting too high. Metformin decreases the amount of glucose your body absorbs from things you eat and drink. Metformin reduces the amount of glucose that your liver makes. Metformin also helps your body’s own insulin to work better. (Insulin is a hormone that helps your body use glucose as a source of energy.) How is metformin supplied (dosage forms)? Metformin is available as Fortamet, Glumetza, and generic metformin in the following dosage forms that are taken by mouth. 500 mg, 625 mg, 750 mg, 850 mg, 1000 mg oral tablets 500 mg, 750 mg, 1000 mg extended-release oral tablets 500 mg/5 mL oral solution How should I store metformin? Metformin should be stored at room temperature, between 68 F to 77 F (20 C to 25 C). It can be exposed to temperatures between 59 F to 86 F (15 C to 30 C), for shorter periods of time, such as when transporting it. Store in a cool, dry place.
HOW TO USE: liquid or tablet that is swallowed
SIDE EFFECTS: What are the most common side effects of metformin? The most common side effects of metformin are listed below. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any of these side effects that bother you. Diarrhea Nausea or vomiting Gas or feeling bloated Feeling unusually weak or tired Stomach pain, upset stomach, heartburn Headache Constipation Change in how things taste or a metallic taste Infection in the nose or throat, sore throat, or common cold symptoms There may be other side effects of metformin that are not listed here. Contact your healthcare provider if you think you are having a side effect of a medicine. In the U.S., you can report side effects to the FDA at www.fda.gov/medwatch or by calling 800-FDA-1088. In Canada, you can report side effects to Health Canada at www.health.gc.ca/medeffect or by calling 866-234-2345. What are the serious side effects of metformin? While less common, the most serious side effects of metformin are described below, along with what to do if they happen. Severe Allergic Reactions. Metformin may cause allergic reactions , which can be serious. Stop using metformin and get help right away if you have any of the following symptoms of a serious allergic reaction. Breathing problems or wheezing Racing heart Fever or general ill feeling Swollen lymph nodes Swelling of the face, lips, mouth, tongue, or throat Trouble swallowing or throat tightness Itching, skin rash, or pale red bumps on the skin called hives Nausea or vomiting Dizziness, feeling lightheaded, or fainting Stomach cramps Joint pain Lactic Acidosis. Metformin may cause lactic acidosis (a buildup of lactic acid in your blood), which can be serious. Stop using metformin and get help right away if you have any of the following symptoms of lactic acidosis. General ill feeling Muscle pain Difficulty breathing Drowsiness Stomach pain Vitamin B12 Deficiency . Metformin may cause you to have low levels of vitamin B12 in your blood (possibly by decreasing the amount of vitamin B12 your body absorbs from things you eat or drink), which may lead to anemia (low levels of red blood cells). Your healthcare provider will likely use lab tests to check your vitamin B12 levels and for anemia. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms of anemia. Unusual weakness or tiredness Cold hands and feet Fast or abnormal heartbeat Pale or yellowish skin Dizziness, lightheadedness, or feeling like you are about to pass out Shortness of breath Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia). When metformin is used with insulin or other medicines that lower your blood sugar by increasing your body’s own insulin levels, it can cause hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). The doses of the other medicines may need to be changed when taken with metformin. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms of low blood sugar. Headache Crankiness or anxiety Hunger Dizziness or confusion Blurry vision Slurred speech Sweating Feeling jittery or shakiness Fast heartbeat Seizures
PRECAUTIONS: Who should not use metformin? Allergies to Ingredients. People who are allergic to any of the following should not take metformin. Metformin Fortamet Glumetza Any of the ingredients in the specific product dispensed Your pharmacist can tell you all of the ingredients in the specific metformin products they stock. Kidney Problems. Metformin should not be used if your kidneys are not working as well as they should be. If there is a concern about the health of your kidneys, your healthcare provider may do tests to determine if they are working well enough to take this medicine. Metabolic Acidosis, Including Diabetic Ketoacidosis. Metformin should not be used in people with acute or chronic metabolic acidosis (when the chemical balance of acids and bases in your blood gets thrown off). Tell your healthcare provider if you have a history of metabolic acidosis or diabetic ketoacidosis . What should I know about metformin before using it? Do not take metformin unless it has been prescribed to you by a healthcare provider. Take it as prescribed. Do not share metformin with other people, even if they have the same condition as you. It may harm them. Keep metformin out of the reach of children. Take metformin with meals to help decrease the chance you will have an upset stomach. Certain forms of metformin should be taken with the evening meal. Ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider about the best way to take your medicine. If you take the liquid form of metformin, use an accurate measuring device to measure your dose. A household spoon is not an accurate measuring device and may cause you to take the wrong dose. Ask your pharmacist to recommend an appropriate measuring device. If you take an oral tablet form of metformin, you may sometimes notice something in your stool (poop) that looks like the tablet. This is normal and should not cause concern. Do not chew, cut, or crush extended-release metformin tablets, they should be swallowed whole. Metformin can cause ovulation (release of an egg from your ovary) if you have not gone through menopause, even if you do not have regular periods. This can increase your chance of getting pregnant. Certain conditions that cause increased stress on your body, like fever, trauma (such as a car accident), infection, or surgery, can change the amount of diabetes medicines you need to take to control your diabetes. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have any of these conditions to decide if your medicine needs to be changed. Talk to your healthcare provider about how to prevent, recognize, and manage low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), high blood sugar (hyperglycemia), and diabetes-related problems. People who are 65 years or older can be at greater risk for some side effects from metformin. Talk to your healthcare provider about your risks if you are in this age group. What should I tell my healthcare provider before using metformin? Tell your healthcare provider about all of your health conditions and any prescription or over-the-counter (OTC) medicines, vitamins/minerals, herbal products, and other supplements you are using. This will help them determine if metformin is right for you. In particular, make sure that you discuss any of the following. Liver Problems. Tell your healthcare provider if you have liver problems. Your risk of lactic acidosis is increased if your liver is not working as well as it should be. Current and Past Medical Conditions. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any of the following. Kidney problems Heart problems, including congestive heart failure or a heart attack Drink alcohol often or in large amounts Have an upcoming medical test that uses contrast (a special dye), surgery, or other procedure Dehydration Severe infection Stroke Other Medicines and Supplements. Metformin may interact with other medicines and supplements. Before taking metformin, tell your healthcare provider about any prescription or over-the-counter (OTC) medicines, vitamins/minerals, herbal products, and other supplements you are using. See the Interactions section for more details. Pregnancy. It is not known if or how metformin could affect pregnancy or harm an unborn baby. Tell your healthcare provider if you are or plan to become pregnant. Your healthcare provider will advise you if you should take metformin while you are pregnant or trying to get pregnant. Breastfeeding. Metformin passes into breast milk, but the effects on the baby or on milk production are not clear. Tell your healthcare provider if you are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Your healthcare provider will advise you if you should take metformin while breastfeeding.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: Does metformin interact with foods or drinks? There are no known interactions between metformin and foods or drinks. Alcohol can increase the risk of lactic acidosis (a serious side effect of metformin discussed above). It is unknown if drinking alcohol will affect metformin in other ways, but alcohol may affect blood sugar levels in people with diabetes. This may interfere with the effect of metformin. It is best to limit the amount of alcohol you drink. Does metformin interact with other medicines (drug interactions)? Always tell your healthcare provider about any prescription or over-the-counter (OTC) medicines, vitamins/minerals, herbal products, and other supplements you are using. In particular, make sure that you discuss if you are using any of the following before using metformin. A carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, such as zonisamide (Zonegran), acetazolamide (Diamox), or methimazole Medicines to treat diabetes, especially insulin or medicines that increase your insulin levels Many other medicines can increase your blood sugar and can interfere with the effect of metformin. Talk to your pharmacist or healthcare provider before starting or stopping other medicines while taking metformin. You may need to monitor your blood sugar levels more closely during these times. Some other medicines may alter the blood levels of metformin. Tell your healthcare provider about all medicines that you take or have recently taken.
OVERDOSE: What should I do if I accidentally use too much metformin? If you or someone else has taken too much metformin, get medical help right away, call 911, or contact a Poison Control center at 800-222-1222. What should I do if I miss a dose of metformin? If you miss a dose, take your next dose as you normally would unless your healthcare provider tells you something different. Do not take double or extra doses.
Formulary
Adding plans allows you to compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
To view formulary information first create a list of plans. Your list will be saved and can be edited at any time.
Adding plans allows you to:
- View the formulary and any restrictions for each plan.
- Manage and view all your plans together – even plans in different states.
- Compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
- Access your plan list on any device – mobile or desktop.






