This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Exploring the antidepressant effects of oleacein, a rare compound found in olives

Researchers are exploring natural compounds as potential alternatives to conventional antidepressants, which often yield inconsistent results. Compounds that activate the TrkB receptor are of particular interest, as this receptor stimulates the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a molecule believed to play a crucial role in preventing and treating neuroinflammation and depression.
Due to its structural similarity to oleocanthal, a compound known for its anti-inflammatory properties, oleacein (OC) is considered a promising candidate for combating inflammation-induced depression.
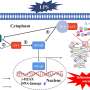
A new study published in Cell Communication and Signaling has found that treating SH-SY5Y cells, a human neuronal model, with OC leads to an increase in the expression of the BDNF gene. A thorough gene expression analysis revealed the activation of the cell cycle and neurogenesis/maturation processes, along with a decrease in the inflammatory response.
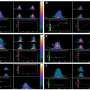
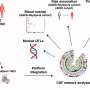
A single oral dose of OC increased BDNF expression in the brain of a transgenic mouse model, which suggests the activation of the TrkB receptor. In a mouse model where depression-like symptoms were induced by a bacterial toxin called lipopolysaccharide (LPS), mice given oral OC for 10 consecutive days beforehand exhibited less depressive behavior in a tail suspension test compared to control mice.
OC administration also decreased the LPS-induced overexpression of inflammatory cytokine genes (Tnfα, Il1β, and Il6) and reversed the LPS-induced decrease in Bdnf expression in the hippocampus of the mouse brain. Gene expression profiling of the brain hippocampus indicated that OC treatment regulated BDNF/TrkB-stimulated signaling pathways. Similar results were confirmed in SH-SY5Y cells cotreated with OC/LPS.
These findings suggest that OC may offer a protective effect against depression induced by neuroinflammation.
More information: Daiki Wakasugi et al, A rare olive compound oleacein functions as a TrkB agonist and mitigates neuroinflammation both in vitro and in vivo, Cell Communication and Signaling (2024). DOI: 10.1186/s12964-024-01691-x