This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Discovery of key target for precision pharmacology makes ideal candidate to treat heart failure

Researchers at the University of Houston College of Pharmacy have discovered that when a higher amount of a protein called AKAP12 is present inside the heart, it speeds up the work of an enzyme called PDE8A and can accelerate cardiac dysfunction.
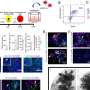
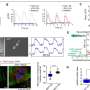
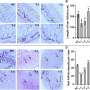
In the journal Circulation Research Bradley McConnell, a University of Houston professor of pharmacology, and Hanan Qasim, the first author of the study and a doctoral student while in the McConnell lab, reported that increased activity of AKAP12 in cardiac myocytes (the cells responsible for contraction of the heart) significantly reduces contractility.
The team also found this reduced contractility can be reversed by inhibiting PDE8A, which McConnell and Qasim also identified as located near AKAP12.
"We are the first to demonstrate that AKAP12 upregulation in cardiac tissue accelerates cardiac maladaptive remodeling. Very interestingly, we also found that patients with end-stage heart failure have upregulated gene and protein levels of AKAP12," reports McConnell and Qasim. "AKAP12 makes an appealing target for precision pharmacology and can be used as a therapeutic target for the treatment of heart failure."
More than 6 million adults in the United States have heart failure, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Also known as congestive heart failure, it is a condition that develops when your heart doesn't pump enough blood for your body's needs.
AKAPs (A-kinase anchoring proteins) are a class of scaffolding proteins that form centers (signalosomes) that regulate cardiac function in the heart. Specifically, it creates AKAP12 and β2AR (β2-adrenergic receptor), both of which are important for cardiac contractility.
However, the role of cardiac AKAP12 has been unclear.
"Thus, our objective was to investigate whether cardiac myocyte AKAP12 upregulation reduces cardiac contractility by reducing intracellular cAMP levels downstream of the stimulated β2AR," said McConnell. A common secondary messenger, cAMP mediates many biological responses.
"Current therapeutics have many off-target pharmacological effects, which could be reduced by subcellular drug delivery. Hence, AKAPs that form microdomains within the cells have been suggested as targets for precision pharmacology, and AKAP12 may be a good candidate for ameliorating heart failure," McConnell said.
Also on the team are three current graduate students in the McConnell lab: Ying Xu, Mehrdad Rajaei, and Hala Abdelnassar.
"This is a very important finding, not only because of its novelty and impact on the field but also because this study involved graduate students working together in a very collaborative and supportive manner—a demonstration that working together brings success," McConnell added.
More information: Hanan Qasim et al, AKAP12 Upregulation Associates With PDE8A to Accelerate Cardiac Dysfunction, Circulation Research (2024). DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.323655