1.0 Senior Commanders
There are a number of senior military officers with a direct and indirect impact on the British Army’s military training curriculum across the spectrum of Phase 1, Phase 2 and Phase 3 training.
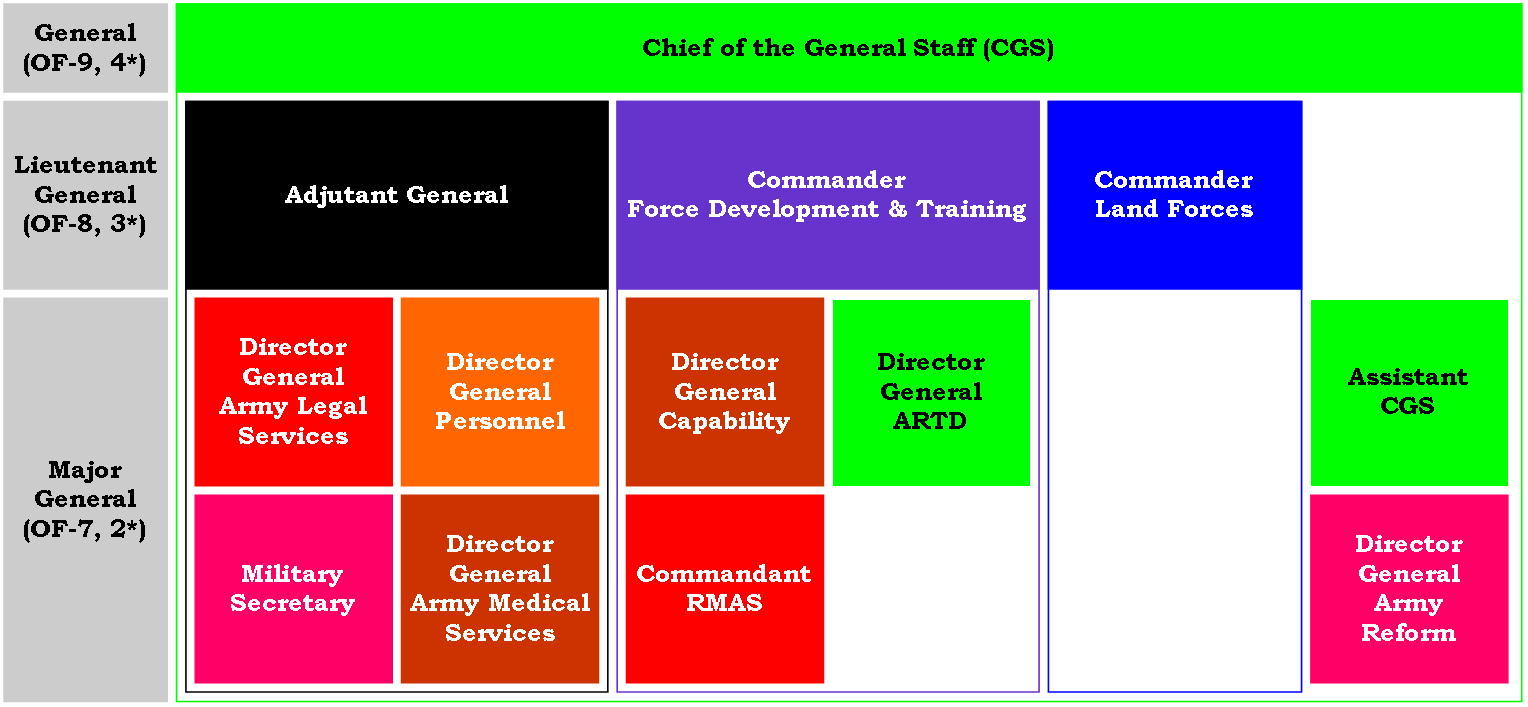
Figure 1 outlines the senior military officers at the General (OF-9) to Major General (OF-7) level and their respective chains of command.
Figure 1: Senior military officers (OF-9 to OF-7)
2.0 Chief of the General Staff
The Chief of the General Staff (CGS), a General (OF-9), is the professional head of the Army. CGS is responsible for generating a balanced and integrated Army capability, and for maintaining the fighting effectiveness, efficiency and morale of the Service. CGS reports to the Chief of the Defence Staff (CDS). As a member of the Defence Council and the Army Board, the Defence Ministerial Committee, the Defence Board, the Chiefs of Staff Committee and the Senior Appointments Committee CGS contributes to the conduct of Defence higher level business, with a particular responsibility for providing specialist advice on Army matters. CGS chairs the Executive Committee of the Army Board.
3.0 Adjutant General
As the Army’s Principal Personnel Officer, the Adjutant General, a Lieutenant General (OF-8), has three distinct functions:
- Support the delivery of a sufficient number of capable and motivated personnel;
- Lead the Army’s Personnel and Infrastructure Lines of Development (PILOD);
- On behalf of Defence, provide the policy lead for Children and Young people and the Army’s Cadet Forces.
These functions are carried out in order to enhance and sustain the operational effectiveness of the Army, now and in the future.
Figure 2 outlines the senior military officers within the Adjutant General’s chain of command at the Major General (OF-7) to Brigadier (OF-6) level.
Figure 2: Senior military officers in the Adjutant General’s chain of command
3.1 Director General Army Legal Services
The primary role of the Director General of the Army Legal Services (DG ALS), a Major General (OF-7), is to deliver military legal support to the Army. However, DG ALS is also responsible for the force generation of ALS personnel (i.e. sufficient, motivated and trained) as Service Director and Head of Arm for the ALS.
3.2 Director Legal Advisory
The Director Legal Advisory, a Brigadier (OF-6), is a 1* staff directorate in Army HQ that delivers military legal support to Army HQ and its chain of command on discipline and administrative law, employment law and legislation and training.
3.3 Director General Army Medical Services
The overarching role of the Director General Army Medical Services (DGAMS), a Major General (OF-7), is to monitor and assess the health of the Army to assist DG Pers in the provision of Health Policy. However, DG AMS also provides a policy oversight and assurance for CGS in the generation and delivery of medical operational capability.
This post is to be downgraded to Brigadier (OF-6) level by December 2015.
3.4 Director Medical Capability (Army)
The Director Medical Capability (Army) (D Med Plans(A)), a Brigadier (OF-6), supports DG AMS in the development of medical operational concepts, doctrine and capability, health advice and healthcare policy in order to meet the requirements of the Army and Defence. D Med Plans(A) also develops Land Forces’ medical operational capability in order to meet Army and Defence requirements.
This post is to be downgraded to Colonel (OF-5) level officer by December 2015.
3.5 Military Secretary
The role of the Military Secretary, a Major General (OF-7), is to develop, manage and guide the careers of all officers and soldiers, giving due weight to the needs of the Army and the individual, with the overriding purpose of enhancing the operational effectiveness of the Army.
In a nutshell, the Military Secretary supports the Army’s operational effectiveness by matching the right people, regular and reservists, to the right posts, and giving them timely notice
3.6 Deputy Military Secretary
The Deputy Military Secretary, a Brigadier (OF-6), holds responsibility for the career management and development of officers (below Major General) and all soldiers in the Army, both Regular Army and Army Reserve. The mission of the Deputy Military Secretary is to develop, manage and guide the careers of all officers and soldiers, giving due weight to the needs of both the Army and the individual, with the overriding purpose of enhancing the operational effectiveness of the Army.
3.7 Director General Personnel
The Director General Personnel (DG Pers), a Major General (OF-7), as the 2* lead for the personnel function in the Army staff, is to develop and deliver personnel policies, plans and services, and represent the Army’s personnel needs in the tri-Service, Defence and cross-Government arenas in order to sustain and enhance the operational effectiveness of the Army.
3.8 Director Personnel Operations
Directors Personnel Operations will cohere and integrate operationally and non-operationally focused regimental functions vested in the Corps Colonels, command DCAMUS, Colonel AGC (Adjutant General’s Corps) and Colonel BG (Brigade of Gurkhas) and deliver staff outputs for Heritage, PS12 (Ceremonial), repatriation and the Army Inquiries and Aftercare Support Cell (AI & ASC).
3.9 Director Personnel Capability
The role of the Director Personnel Capability, a Brigadier (OF-6), is to develop Army personnel strategy and engage with Defence and the other services to shape and influence strategic personnel direction and the delivery of joint effects, in order to sustain and enhance the operational effectiveness of the Army.
3.10 Director Manning (Army)
The role of the Director Manning (Army) (DM(A)), a Brigadier (OF-6), is to develop and direct manning and employment, and health policy and plans, in order to sustain the Army manpower component of Defence capability, now and in the future.
3.11 Director Personnel Services (Army)
The role of the Director Personnel Services (Army) (DPS(A)), a Brigadier (OF-6), is to develop policy for the promotion of the Army’s ethos, the maintenance of discipline, and the development and delivery of the Army’s conditions of service, in order to sustain the motivation and well being of the Army.
3.12 Director Staff Personnel and Support (Army)
The Director Staff and Personnel Support (Army) DSPS(A), a Brigadier (OF-6), via the HQ DSPS(A) is the lead staff branch in Army HQ on military human resources (HR) delivery and associated issues. It provides the Army with holistic and timely policy, direction and professional advice on all aspects of personnel administration (including delivery of pay, allowances, charges, public and non-public funds) and staff support to units and formations. In addition, as an Arms and Service Directorate, it is also responsible for sustaining the military capability of SPS Branch personnel (Regular and Reserves) across all the DLoDs (Defence Lines of Development).
3.13 Chief of Staff Personnel and Support Command
The role of the Chief of Staff Personnel and Support Command (PSC) is to direct and coordinate the staff output within PSC in order to support the generation of operational capability.
3.14 Director Educational and Training Services (Army)
The Director Educational and Training Services (DETS(A)), a Brigadier (OF-6), is responsible for Army Educational Policy and provides functional direction to and assurance of Army Educational and Training Services. DETS(A) delivers subject matter expertise for Army/MOD/OGD, external stakeholders, professional bodies and other Armed Forces. DETS(A) is also the lead proponent for cultural and language capability; Army Library and Information Services; Accreditation.
4.0 Commander Force Development and Training
The role of the Commander Force Development and Training (FDT), a Lieutenant General (OF-8), is to optimise the delivery of Army capability in order to ensure success on operations now and in the future.
The Commander FDT is assisted by three Major Generals (OF-7) in the delivery of Army capability.
- Commandant Royal Military Academy Sandhurst;
- Director General Capability; and
- Director General Army Recruiting and Training Division.
Figure 3 outlines the senior military officers within the Commander FDT’s chain of command at the Major General (OF-7) to Brigadier (OF-6) level.
Figure 3: Senior military officers in the Commander FDT’s chain of command
4.1 Chief of Staff Force Development and Training
The role of the Chief of Staff Force Development and Training (CoS FDT), a Brigadier (OF-6), is to direct and coordinate the staff output within FDT to optimise the delivery of Army capability through coherent support to subordinate and superior organisations.
4.2 Director Force Development
The role of the Director Force Development (D FD), a Brigadier (OF-6), is to set the long term agenda for Army Transformation. The directorate looks out to the medium and long term in order to identify trends and drivers that will impact on future force development in its widest sense. It is a cross DLOD activity and enables DGLW to offer evidentially based advice to Commander FDT as the post-holder sets priorities across the command and as they seek to influence senior decision makers in both the Army and Defence.
4.3 Head Information Superiority
The Head Information Superiority, a Brigadier (OF-6), is the focal point for all ISTAR policy, planning, doctrine, training and equipment capability matters within Army HQ.
4.4 Commandant Royal Military Academy Sandhurst
The role of the Commandant Royal Military Academy Sandhurst (RMAS), a Major General (OF-7), is to train and educate sufficient quality Regular Army/Army Reserve officers and soldiers in order to support the operational requirements of the Army and Defence.
4.5 Director General Army Recruiting and Training Division
The role of the Director General Army Recruiting and Training Division (DG ARTD), a Major General (OF-7), is to deliver the required number of appropriately trained and motivated officers and soldiers in order to meet the current and future operational requirements of the Army and Defence.
4.6 Director Recruit Training (Operations)
The role of the Director Recruit Training (Operations), a Brigadier (OF-6), is to:
- Plan and execute the Army’s national recruiting campaign;
- Provide functional support and co-ordination to the regional chain of command executing the regional element of the Army’s national recruitment campaign;
- Deliver the required number of appropriately trained and motivated service personnel; and
- Direct and manage the recruiting, development, selection and training pipeline.
4.7 Director Recruit Training (Support)
The role of the Director Recruit Training (Support), a SCS1 (OF-6), is to provide direction and support to all divisional activities in accordance with DGARTs intent and in conjunction with COS.
4.8 Commander Defence College of Logistics and Personnel Administration
The role of the Commander Defence College of Logistics and Personnel Administration (DCLPA), a Brigadier (OF-6), is to deliver integrated logistic support and personnel administration training to all four services to the quantity and standards directed by the TDA and TRA in order to support the operational requirements of Defence. Finally, Commander DCLPA is to act as Garrison Commander for Deepcut, Pirbright and Mychett.
4.9 Commander Initial Training Group
The role of the Commander Initial Training Group (ITG), a Brigadier (OF-6), is to train Regular Army and Army Reserve soldiers to the quantity and standards directed by the Training Delivery Authority (TDA) and the Training Requirements Authority (TRA) in order to prepare them for Phase 2 training. As such, ITG delivers relevant, progressive, challenging and safe training for Regular Army and Army Reserve soldiers, facilitating their successful transition to Phase 2 training. Through Values Based Leadership by inspirational Permanent Staff, ITG lays the foundations of military character in Soldiers under Training (SUT). By contextualising the soldiers’ education and training, ITG prepares soldiers both for Phase 2 training and subsequent operations.
4.10 Commandant School of Infantry
The role of the Commandant School of Infantry, a Brigadier (OF-6), is to deliver trained officers and soldiers in accordance with the statement of training requirement in order to support the operational requirements of the Army and Defence. The School of Infantry trains and qualifies officers, warrant officers, non-commissioned officers, other ranks, and recruits for the Infantry and wider Army in battlefield leadership and dismounted close combat. It does this in three principal establishments:
- The Infantry Training Centre at Catterick;
- The Infantry Battle School at Brecon; and
- The Support Weapons School at Warminster.
4.11 Commandant Royal Military School of Engineering
The role of the Commandant Royal School of Military Engineering (RSME), a Brigadier (OF-6), is to provide training in all engineering disciplines, which provide the unique range of skills that are fundamental to the Military Engineer as well as delivering Military working animals, handlers and maintainers. Military Engineer skills include the command and management of engineer tasks, combat engineering, artisan, technical and professional engineering, communication, watermanship and driving specialist engineer vehicles.
4.12 Director Training (Army)
The role of Director Training (Army) (D Trg(A)), a Brigadier (OF-6), is to provide the Army HQ’s 1* focal point for the Training Line of Development (TLoD). Part of Army HQ, D Trg(A) comprises of four staff branches:
- Individual Training;
- Training Development;
- Training Capability; and
- Collective Training.
4.13 Director General Capability
The role of the Director General Capability (DG Cap), a Major General (OF-7) is to lead the Army’s Force Development, Capability Development and Warfare Development effort in order to ensure success on current and future operations.
4.14 Capability Director Combat
The role of the Capability Director Combat, a Brigadier (OF-6), is to drive a process of capability development that is:
- Led by force design;
- Sets properly designed and costed Key User Requirements;
- Is effectively integrated and coherent across DLOD (Defence Lines of Development);
- Is underpinned by thorough investigation and analysis;
- Identifies the capabilities required for the future (expressed as functional concepts, CONEMPs and CONUSEs); and
- Contributes to the construction of a balanced and affordable Land Programme.
4.15 Capability Director Combat Support
The role of the Capability Director Combat Support, a Brigadier (OF-6), is the same as the Capability Director Combat (Section 4.13).
4.16 Capability Director Information
The role of the Capability Director Information, a Brigadier (OF-6), is to lead development and X-DLOD Integration of designated deployable C4ISR capabilities in order to enable success on operations, now and in the future.
4.17 Capability Director Combat Service Support
The role of the Capability Director Combat Support, a Brigadier (OF-6), is the same as the Capability Director Combat (Section 4.13).
4.18 Commander Collective Training Group
The role of the Commander Collective Training Group (CTG), a Brigadier (OF-6), is to deliver to the Field Army and others the most effective education, training and training support within resources in order to prepare force elements to succeed on current, contingent and future operations. It is also to deliver a coherent and relevant training progression across the Collective Training Establishments (CTEs), and fulfil responsibilities for the construct and refine functions of collective training in accordance with Collective Training Governance.
4.19 Capability Management Review Force Development and Training
The Brigadier (OF-6) in charge of this review is to conduct a Capability Management Review (CMR) to test the outputs, structures and ways of working of the capability management function (focussing initially on the Direct, Develop, and Deliver (D3) functions) within FDT.
This is a ‘Lifed’ post meaning it will cease to exist at the end of the review.
4.20 Director Land Warfare
The role of the Director Land Warfare, a Brigadier (OF-6), is to lead Warfare Development involving:
- The production and advocacy of relevant Tactical Doctrine;
- The systematic utilisation of experience;
- Driving the learning of lessons pan capability and DLOD (Defence Lines of Development);
- Ensuring individual and collective training is teaching what they should; and
- The provision of a reach-back focus for deployed/deploying formations and units.
5.0 Commander Land Forces
Although the Commander Land Forces (CLF), a Lieutenant General (OF-8), has a number of functions, the relevant function regarding training include:
- Develop a land force collective training strategy; and
- Develop Reserve Forces.
Figure 4 outlines the senior military officers within the CLF’s chain of command at the Major General (OF-7) to Brigadier (OF-6) level.
5.1 Chief G7 Training & Development (HQ Allied Rapid Reaction Corps)
The role of the Chief G7, a Brigadier (OF-6) is to coordinate and oversee training and development within the Allied Rapid Reaction Corps in order to prepare the headquarters for forthcoming deployments and commitments, thereby contributing towards the UK military commitment to NATO.
5.2 Chief Personnel and Logistics (HQ Allied Rapid Reaction Corps)
The role of the Chief Personnel and Logistics, a Brigadier (OF-6) is to coordinate and deliver all support activity within HQ Allied Rapid Reaction Corps to optimise the military capability within the Allied Rapid Reaction Corps in order to contribute towards the UK military commitment to NATO.




Thank you very much, Andrew!
Where is figure 4 which outlines the senior military officers within the CLF’s chain of command?
Hi Radu,
Simple Answer: Apologies, I forgot!
Longer Answer: At the time of writing the CLF was undergoing some changes, so I worked on the assumption I would update the article (or Figure 4) at a later date. However, I subsequently became preoccupied with other articles. After recently emigrating to Australia, I am today moving from short-term to long-term accommodation. From today I will be without internet access for approximately 1 week whilst I get set-up in my new home! I will update at the earliest opportunity.