Dosing & Uses
Dosage Forms & Strengths
injectable solution
- 20mg/mL
tablets
- 10mg
- 25mg
- 50mg
- 100mg
Severe Essential Hypertension
10 mg PO q6hr for 2-4 days; 25 mg q6hr daily for the first week; increase to 50 mg q6hr from second week on; adjust dose to lowest effective levels
20-40 mg IM/IV; repeat as necessary
Dosing considerations
- Change to oral therapy as soon as possible
Hypertension (Chronic)
Initial: 10 mg PO q6hr for 2-4 days; may increase gradually by 10-25 mg/dose every 2-5 days up to 50 mg PO q6hr (some patients require 300 mg/day)
See also combo with isosorbide dinitrate
Hypertensive Crisis
10-40 mg IV/IM; not to exceed 20 mg/dose; repeat PRN
Pregnancy-associated
- 5-10 mg IV/IM initially, THEN 5-10 mg q20-30min PRN, OR
- 0.5-10 mg/hr IV infusion
Congestive Heart Failure
Initial dose: 10-25 mg PO q6-8hr; titrate dose q2-4weeks
Maintenance dose: 225-300 mg/day PO divided q6-8hr
Dosing considerations
- Adjust dose per individual response
Dosage Forms & Strengths
injectable solution
- 20mg/mL
tablets
- 10mg
- 25mg
- 50mg
- 100mg
Severe Essential Hypertension
1.7-3.5 mg/kg/day IM or IV divided in 4-6 doses.
Heart Failure, Afterload Reduction
Infants: 0.1-0.5 mg/kg/dose IV q6-8hr; not to exceed 2 mg/kg/dose
Children and adolescents: 0.15-0.2 mg/kg/dose IV q4-6hr; not to exceed 20 mg/dos
Oral administration
- Infants and older: 0.75-3 mg/kg/day PO divided q6-12hr; not to exceed 200 mg/day or 7 mg/kg/day
Hypertensive Crisis
Infants or older: 0.1-0.2 mg/kg IV/IM q4-6hr PRN initially; may increase to usual dose of 1.7-3.5 mg/kg/day divided q4-6hr; not to exceed 20 mg/dose IM or IV or 2 mg/kg q3-6hr with cumulative dose not to exceed 9 mg/kg
Hypertension (Chronic)
Initial: 0.75-1 mg/kg/day PO divided q6-12hr
Maximum dose in infants (<1 year): 5 mg/kg/day PO divided q6-12hr
Maximum dose in children (>1 year): 7.5 mg/kg/day PO divided q6-12hr; not to exceed 200 mg/day
Increase gradually over 3-4 weeks
Interactions
Interaction Checker
No Results

Contraindicated
Serious - Use Alternative
Significant - Monitor Closely
Minor

Contraindicated (0)
Serious - Use Alternative (4)
- lofexidine
lofexidine, hydralazine. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration with other drugs that decrease pulse or blood pressure to mitigate risk of excessive bradycardia and hypotension.
- lonafarnib
hydralazine will increase the level or effect of lonafarnib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration of lonafarnib (a sensitive CYP3A substrate) with weak CYP3A inhibitors is unavoidable, reduce to, or continue lonafarnib at starting dose. Closely monitor for arrhythmias and events (eg, syncope, heart palpitations) since lonafarnib effect on QT interval is unknown.
- pexidartinib
hydralazine and pexidartinib both increase Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Pexidartinib can cause hepatotoxicity. Avoid coadministration of pexidartinib with other products know to cause hepatoxicity.
- pretomanid
hydralazine, pretomanid. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Pretomanid regimen associated with hepatotoxicity. Avoid alcohol and hepatotoxic agents, including herbal supplements and drugs other than bedaquiline and linezolid.
Monitor Closely (108)
- acebutolol
hydralazine increases effects of acebutolol by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Additive hypotensive effects.
- aceclofenac
aceclofenac decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- acemetacin
acemetacin decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- aldesleukin
aldesleukin increases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypotension.
- amifostine
amifostine, hydralazine. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration with blood pressure lowering agents may increase the risk and severity of hypotension associated with amifostine. When amifostine is used at chemotherapeutic doses, withhold blood pressure lowering medications for 24 hr prior to amifostine; if blood pressure lowering medication cannot be withheld, do not administer amifostine.
- amphetamine
hydralazine, amphetamine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sympathomimetics can antagonize the activity of some antihypertensive agents.
hydralazine, amphetamine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypertension. - aspirin
aspirin decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- aspirin rectal
aspirin rectal decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- aspirin/citric acid/sodium bicarbonate
aspirin/citric acid/sodium bicarbonate decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- atenolol
hydralazine increases effects of atenolol by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Additive hypotensive effects.
- atogepant
hydralazine will increase the level or effect of atogepant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- avanafil
avanafil increases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypotension.
- axitinib
hydralazine increases levels of axitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- benzphetamine
hydralazine, benzphetamine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypertension.
- betaxolol
hydralazine increases effects of betaxolol by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Additive hypotensive effects.
- bisoprolol
hydralazine increases effects of bisoprolol by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Additive hypotensive effects.
- bretylium
hydralazine, bretylium. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Each drug may cause hypotension.
- carbidopa
carbidopa increases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Therapy with carbidopa, given with or without levodopa or carbidopa-levodopa combination products, is started, dosage adjustment of the antihypertensive drug may be required.
- carvedilol
carvedilol, hydralazine. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Additive hypotensive effects.
- celecoxib
celecoxib decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- choline magnesium trisalicylate
choline magnesium trisalicylate decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- dexfenfluramine
hydralazine, dexfenfluramine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypertension.
- dexmethylphenidate
hydralazine, dexmethylphenidate. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sympathomimetics can antagonize the activity of some antihypertensive agents.
- dextroamphetamine
hydralazine, dextroamphetamine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sympathomimetics can antagonize the activity of some antihypertensive agents.
- diclofenac
diclofenac decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- diethylpropion
hydralazine, diethylpropion. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sympathomimetics can antagonize the activity of some antihypertensive agents.
- diflunisal
diflunisal decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- dobutamine
hydralazine, dobutamine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sympathomimetics can antagonize the activity of some antihypertensive agents.
- dopamine
hydralazine, dopamine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sympathomimetics can antagonize the activity of some antihypertensive agents.
- ephedrine
hydralazine, ephedrine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sympathomimetics can antagonize the activity of some antihypertensive agents.
- epinephrine
hydralazine, epinephrine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sympathomimetics can antagonize the activity of some antihypertensive agents.
- epoprostenol
epoprostenol, hydralazine. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- esmolol
hydralazine increases effects of esmolol by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Additive hypotensive effects.
- etodolac
etodolac decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- fenfluramine
hydralazine, fenfluramine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypertension.
- fenoldopam
fenoldopam, hydralazine. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fenoprofen
fenoprofen decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- finerenone
hydralazine will increase the level or effect of finerenone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor serum potassium during initiation and dosage adjustment of either finererone or weak CYP3A4 inhibitors. Adjust finererone dosage as needed.
- flibanserin
hydralazine will increase the level or effect of flibanserin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased flibanserin adverse effects may occur if coadministered with multiple weak CYP3A4 inhibitors.
- flurbiprofen
flurbiprofen decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- ibuprofen
ibuprofen decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- ibuprofen IV
ibuprofen IV decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- iloprost
iloprost, hydralazine. Either increases effects of the other by additive vasodilation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. When administering iloprost IV, consider temporary discontinuation of concomitant vasodilators or other medications that reduce blood pressure to mitigate potential additive hypotensive effects. If hypotension persists despite discontinuing other antihypertensives and fluid resuscitation, consider iloprost dose reduction or discontinuation.
- iloprost inhaled
hydralazine, iloprost inhaled. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- indomethacin
indomethacin decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- isavuconazonium sulfate
hydralazine will increase the level or effect of isavuconazonium sulfate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- isocarboxazid
hydralazine, isocarboxazid. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypertension.
- isoproterenol
hydralazine, isoproterenol. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sympathomimetics can antagonize the activity of some antihypertensive agents.
- ivacaftor
hydralazine increases levels of ivacaftor by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor when coadministered with weak CYP3A4 inhibitors .
- ketoprofen
ketoprofen decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- ketorolac
ketorolac decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- ketorolac intranasal
ketorolac intranasal decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- labetalol
hydralazine increases effects of labetalol by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Additive hypotensive effects.
- lemborexant
hydralazine will increase the level or effect of lemborexant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Lower nightly dose of lemborexant recommended if coadministered with weak CYP3A4 inhibitors. See drug monograph for specific dosage modification.
- levodopa
levodopa increases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Consider decreasing dosage of antihypertensive agent.
- linezolid
hydralazine, linezolid. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypertension.
- lisdexamfetamine
hydralazine, lisdexamfetamine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sympathomimetics can antagonize the activity of some antihypertensive agents.
- lomitapide
hydralazine increases levels of lomitapide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Lomitapide dose should not exceed 30 mg/day.
- lornoxicam
lornoxicam decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- meclofenamate
meclofenamate decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- mefenamic acid
mefenamic acid decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- meloxicam
meloxicam decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- methamphetamine
hydralazine, methamphetamine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sympathomimetics can antagonize the activity of some antihypertensive agents.
- methylenedioxymethamphetamine
hydralazine, methylenedioxymethamphetamine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypertension.
- methylphenidate
hydralazine, methylphenidate. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sympathomimetics can antagonize the activity of some antihypertensive agents.
- metoprolol
hydralazine increases effects of metoprolol by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Additive hypotensive effects.
- midazolam intranasal
hydralazine will increase the level or effect of midazolam intranasal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of mild CYP3A4 inhibitors with midazolam intranasal may cause higher midazolam systemic exposure, which may prolong sedation.
- midodrine
hydralazine, midodrine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sympathomimetics can antagonize the activity of some antihypertensive agents.
- minoxidil
hydralazine, minoxidil. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- mipomersen
mipomersen, hydralazine. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Both drugs have potential to increase hepatic enzymes; monitor LFTs.
- nabumetone
nabumetone decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- nadolol
hydralazine increases effects of nadolol by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Additive hypotensive effects.
- naproxen
naproxen decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- nebivolol
hydralazine increases effects of nebivolol by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Additive hypotensive effects.
- nitroglycerin rectal
nitroglycerin rectal, hydralazine. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Observe for possible additive hypotensive effects during concomitant use. .
- norepinephrine
hydralazine, norepinephrine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sympathomimetics can antagonize the activity of some antihypertensive agents.
- oxaprozin
oxaprozin decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- parecoxib
parecoxib decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- penbutolol
hydralazine increases effects of penbutolol by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Additive hypotensive effects.
- phendimetrazine
hydralazine, phendimetrazine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sympathomimetics can antagonize the activity of some antihypertensive agents.
- phenelzine
hydralazine, phenelzine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypertension.
- phentermine
hydralazine, phentermine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sympathomimetics can antagonize the activity of some antihypertensive agents.
- phenylephrine
hydralazine, phenylephrine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sympathomimetics can antagonize the activity of some antihypertensive agents.
- phenylephrine PO
hydralazine, phenylephrine PO. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypertension.
- pindolol
hydralazine increases effects of pindolol by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Additive hypotensive effects.
- piroxicam
piroxicam decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- procarbazine
hydralazine, procarbazine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypotension.
- propranolol
hydralazine increases effects of propranolol by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Additive hypotensive effects.
- propylhexedrine
hydralazine, propylhexedrine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypertension.
- pseudoephedrine
hydralazine, pseudoephedrine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sympathomimetics can antagonize the activity of some antihypertensive agents.
- salicylates (non-asa)
salicylates (non-asa) decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- salsalate
salsalate decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- serdexmethylphenidate/dexmethylphenidate
hydralazine, serdexmethylphenidate/dexmethylphenidate. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sympathomimetics can antagonize the activity of some antihypertensive agents.
hydralazine, serdexmethylphenidate/dexmethylphenidate. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypertension. - sotalol
hydralazine increases effects of sotalol by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Additive hypotensive effects.
- sulfasalazine
sulfasalazine decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- sulindac
sulindac decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- tadalafil
tadalafil increases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypotension.
- tazemetostat
hydralazine will increase the level or effect of tazemetostat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- timolol
hydralazine increases effects of timolol by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Additive hypotensive effects.
- tinidazole
hydralazine will increase the level or effect of tinidazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tolfenamic acid
tolfenamic acid decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- tolmetin
tolmetin decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
- tranylcypromine
hydralazine, tranylcypromine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypotension.
- treprostinil
hydralazine, treprostinil. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- valoctocogene roxaparvovec
hydralazine and valoctocogene roxaparvovec both increase Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Medications that may cause hepatotoxicity when combined with valoctogene roxaparvovec may potentiate the risk of elevated liver enzymes. Closely monitor these medications and consider alternative medications in case of potential drug interactions.
- xipamide
xipamide increases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- xylometazoline
hydralazine, xylometazoline. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypertension.
- yohimbine
hydralazine, yohimbine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Additive hypotensive effects.
Minor (15)
- agrimony
agrimony increases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- brimonidine
brimonidine increases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- celiprolol
hydralazine increases effects of celiprolol by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- cornsilk
cornsilk increases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- diazoxide
diazoxide, hydralazine. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Additive hypotensive effects.
- forskolin
forskolin increases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- maitake
maitake increases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Maitake mushroom has anti-tumor effects (animal/in vitro research).
- pyridoxine
hydralazine decreases levels of pyridoxine by unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- pyridoxine (Antidote)
hydralazine decreases levels of pyridoxine (Antidote) by unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- reishi
reishi increases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ruxolitinib
hydralazine will increase the level or effect of ruxolitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ruxolitinib topical
hydralazine will increase the level or effect of ruxolitinib topical by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- shepherd's purse
shepherd's purse, hydralazine. Other (see comment). Minor/Significance Unknown. Comment: Theoretically, shepherd's purse may interfere with BP control.
- tizanidine
tizanidine increases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of hypotension.
- treprostinil
treprostinil increases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
Adverse Effects
Frequency Not Defined
Hypotension
Palpitations
Conjunctivitis
Tachycardia
Headache
Peripheral edema
Vascular collapse
Peripheral neuropathy
Anorexia
Diarrhea
Nausea
Vomiting
Psychotic reaction
Agranulocytosis
Leukopenia
Hepatotoxicity
Chest pain
Dyspnea
Nasal congestion
Paralytic ileus
Dysurea
Thrombocytopenia
Peripheral neuritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Agranulocytosis
Arthralgia
SLE syndrome
Warnings
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to hydralazine
Coronary artery disease
Mitral valve rheumatic heart disease
Cautions
May induce SLE-type syndrome (usually at >200 mg/day); instruct patients to report joint/chest pain or fever; discontinue therapy unless benefits outweigh risks; steroid therapy may be necessary long-term
Use caution in CVA, severe renal impairment, volume depletion, preexisting hypotension, concurrency with other hypotensive agents, CAD (potential contraindication)
Use caution in mitral valvular disease; may increase pulmonary artery pressure
Discontinue slowly to avoid rapid rise in blood pressure
Use with caution in patients with pulmonary hypertension; may cause hypotension
Increases fluid and sodium retention; may require treatment or increase in diutretic dose
Peripheral neuritis, including numbness, paresthesia, and tingling, reported; treat symptoms with pyridoxine
Blood dyscarsias, including reduction in red blod cell count, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, reported with therapy; discontinue therapy if any of the hematologic effects occur
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy category: C
Lactation: Excreted in breast milk; use caution
Pregnancy Categories
A: Generally acceptable. Controlled studies in pregnant women show no evidence of fetal risk.
B: May be acceptable. Either animal studies show no risk but human studies not available or animal studies showed minor risks and human studies done and showed no risk. C: Use with caution if benefits outweigh risks. Animal studies show risk and human studies not available or neither animal nor human studies done. D: Use in LIFE-THREATENING emergencies when no safer drug available. Positive evidence of human fetal risk. X: Do not use in pregnancy. Risks involved outweigh potential benefits. Safer alternatives exist. NA: Information not available.Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Direct vasodilator; dilates arterioles with little effect on vein; decreases systemic resistance, which subsequently decreases blood pressure.
Absorption
Bioavailability: Slow acetylator: 30-50%; rapid acetylator: 22-30%
Onset: 5-20 min, maximum effect 10-80 min (IV); 20-30 min (PO)
Duration: 3-8 hr (PO); 1-4 hr (IV)
Distribution
Protein bound: 85-90%
Vd: 0.3-8.2 L/kg
Metabolism
Significantly metabolized in liver by acetylation; slow and rapid acetylator
Metabolites: Phthalazine and pyruvic acid hydrazone metabolites (inactive metabolite)
Elimination
Half-life: 2-8 hr (normal renal function); 7-16 hr (end-stage renal disease)
Excretion: Urine (14%; unchanged)
Pharmacogenomics
HLA-DRw4 appears in 73% of patients experiencing hydralazine-associated SLE
Administration
IV Incompatibilities
Solution: D5W, D10/LR, fructose 10%, fructose 10%/NS
Additive: Aminophylline, ampicillin, chlorothiazide, dobutamine, CaNa2EDTA, ethacrynate, hydrocortisone sodium succinate, mephentermine, methohexital, nitroglycerin, phenobarbital, verapamil
Y-site: Aminophylline, ampicillin, diazoxide, furosemide
IV Compatibilities
Solution: Dextrose-Ringer combinations, D5/LR, dextrose 2.5%/½LR, dextrose-saline combinations, D10W, Ringer, LR, ½NS, NS, Na-lactate 1/6M
Y-site: Heparin, hydrocortisone sodium succinate, nitroglycerin (compatible for 3 hr; may form slight ppt), KCl, verapamil, vit B/C
IV Preparation
Prepare immediately before use
Minimize contact with metal parts during preparation and administration
IV/IM Administration
Administer undiluted IM or as slow IV push directly into vein; in children maximum rate is 5 mg/min; may also administer as continuous infusion
Avoid adding drug to infusion solution
Storage
Store at controlled room temp
Do not refrigerate
Images
| BRAND | FORM. | UNIT PRICE | PILL IMAGE |
|---|---|---|---|
| hydralazine injection - | 20 mg/mL vial |  | |
| hydralazine injection - | 20 mg/mL vial |  | |
| hydralazine injection - | 20 mg/mL vial |  | |
| hydralazine injection - | 20 mg/mL vial |  | |
| hydralazine injection - | 20 mg/mL vial |  | |
| hydralazine injection - | 20 mg/mL vial |  | |
| hydralazine injection - | 20 mg/mL vial |  | |
| hydralazine injection - | 20 mg/mL vial |  | |
| hydralazine injection - | 20 mg/mL vial |  | |
| Hydralazine - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| Hydralazine - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| Hydralazine - | 10 mg tablet | 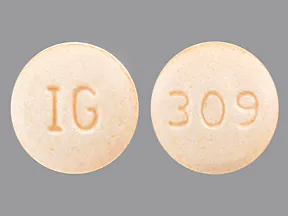 | |
| Hydralazine - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| Hydralazine - | 10 mg tablet |  | |
| Hydralazine - | 25 mg tablet | 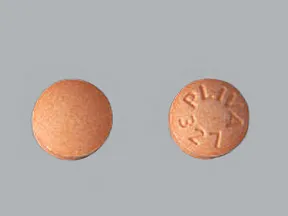 | |
| Hydralazine - | 10 mg tablet | 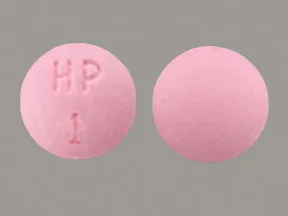 | |
| Hydralazine - | 10 mg tablet | 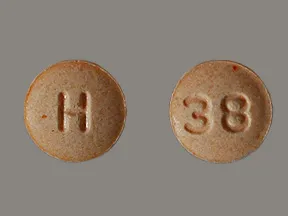 | |
| Hydralazine - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| Hydralazine - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| Hydralazine - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| Hydralazine - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| Hydralazine - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| Hydralazine - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| Hydralazine - | 10 mg tablet |  | |
| Hydralazine - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| Hydralazine - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| Hydralazine - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| Hydralazine - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| Hydralazine - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| Hydralazine - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| Hydralazine - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| Hydralazine - | 10 mg tablet |  | |
| Hydralazine - | 100 mg tablet |  |
Copyright © 2010 First DataBank, Inc.
Patient Handout
hydralazine injection
NO MONOGRAPH AVAILABLE AT THIS TIME
USES: Consult your pharmacist.
HOW TO USE: Consult your pharmacist.
SIDE EFFECTS: Consult your pharmacist.In the US -Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or at www.fda.gov/medwatch.In Canada - Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345.
PRECAUTIONS: Consult your pharmacist.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: Consult your pharmacist.Keep a list of all your medications with you, and share the list with your doctor and pharmacist.
OVERDOSE: If someone has overdosed and has serious symptoms such as passing out or trouble breathing, call 911. Otherwise, call a poison control center right away. US residents can call 1-800-222-1222. Canada residents can call 1-844-764-7669.
NOTES: No monograph available at this time.
MISSED DOSE: Consult your pharmacist.
STORAGE: Consult your pharmacist.Do not flush medications down the toilet or pour them into a drain unless instructed to do so. Properly discard this product when it is expired or no longer needed. Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company for more details about how to safely discard your product.
Information last revised May 2024. Copyright(c) 2024 First Databank, Inc.
IMPORTANT: HOW TO USE THIS INFORMATION: This is a summary and does NOT have all possible information about this product. This information does not assure that this product is safe, effective, or appropriate for you. This information is not individual medical advice and does not substitute for the advice of your health care professional. Always ask your health care professional for complete information about this product and your specific health needs.
Formulary
Adding plans allows you to compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
To view formulary information first create a list of plans. Your list will be saved and can be edited at any time.
Adding plans allows you to:
- View the formulary and any restrictions for each plan.
- Manage and view all your plans together – even plans in different states.
- Compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
- Access your plan list on any device – mobile or desktop.







